1,6-Hexanediol Diglycidyl Ether: Properties and Applications as Cross-linker
Apr 9,2024
General Description
1,6-Hexanediol diglycidyl ether is a versatile compound used as a crosslinking agent and reactive diluent in various industrial applications. It combines the properties of 1,6-hexanediol and glycidyl ether groups to enable polymerization and crosslinking with different substrates, enhancing mechanical properties and chemical resistance. 1,6-Hexanediol diglycidyl ether’s long-chain structure provides flexibility and toughness, making it suitable for durable applications. In specific applications, such as preparing stretched-dried-gel films and hydrophilic nanogels, it plays a crucial role in improving mechanical strength, structural integrity, and biocompatibility. Overall, 1,6-hexanediol diglycidyl ether is essential for creating high-performance materials with tailored properties.

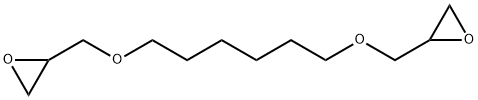
Figure 1. 1,6-Hexanediol diglycidyl ether
Properties
1,6-Hexanediol diglycidyl ether is a versatile chemical compound with a unique structure that plays a crucial role in various industrial applications. This ether is composed of 1,6-hexanediol, a straight-chain diol, and two glycidyl ether groups, which are epoxy-functionalized moieties. The combination of these two components confers unique properties to the molecule, making it an excellent candidate for use as a crosslinking agent or reactive diluent. Due to its reactive epoxy groups, 1,6-hexanediol diglycidyl ether can easily undergo polymerization or crosslinking reactions with a wide range of substrates, including polymers, resins, and oligomers. This versatility allows it to be used in adhesives, coatings, composites, and other materials where enhanced mechanical properties or chemical resistance are desired. Furthermore, the ether's long-chain structure provides flexibility and toughness to the final product, making it suitable for applications that require durability and resilience. Additionally, its low toxicity and good compatibility with various formulations contribute to its widespread use in the chemical industry. In summary, 1,6-hexanediol diglycidyl ether is a highly functional and versatile compound that offers excellent crosslinking and reactive diluent capabilities, making it an essential ingredient in various industrial applications. 1
Applications as cross-linker
Stretched-dried-gel films
1,6-hexanediol diglycidyl ether, as a cross-linker, plays a crucial role in the preparation of highly stretchable and mechanically strong stretched-dried-gel films in gel film fabrication processes. In the study mentioned, various cross-linkers, including 1,6-hexanediol diglycidyl ether, were utilized in the chemical cross-linking of curdlan hydrogels. The resulting self-standing curdlan hydrogels exhibited excellent elongation properties, with elongation strains ranging from 600% to 900% of their original length, irrespective of the specific cross-linker used. When these hydrogels were stretched and dried, stretched-dried-gel films were formed. These films demonstrated significantly enhanced mechanical properties, with tensile strength values between 117-148 MPa and a Young's modulus of 1.6 GPa, compared to non-stretched films. X-ray measurements further revealed that the stretched dried-gel films possessed oriented crystalline domains with an 80% degree of orientation. This indicates that the molecular chains of curdlan were oriented and crystallized during the stretching and drying process, leading to improved tensile strength due to strain-induced crystallization. Therefore, 1,6-hexanediol diglycidyl ether, by facilitating the cross-linking process, contributes to the structural integrity and mechanical strength of the resulting gel films, making it a valuable component in the fabrication of high-performance materials with enhanced properties. 2
Hydrophilic nanogels
1,6-Hexanediol diglycidyl ether serves as a vital cross-linking agent in the preparation of hydrophilic nanogels based on partially hydrolyzed poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline), leading to the formation of biocompatible pseudopolypeptide nanoparticles. The synthesis process takes place in dilute aqueous media, and the presence of 1,6-hexanediol diglycidyl ether as a cross-linker is crucial for nanogel formation. The formation of the nanogels was carefully monitored using dynamic light scattering (DLS) and HSQC NMR spectroscopy, while the resulting nano-objects were thoroughly characterized using a combination of techniques including DLS, TEM, AFM, and NanoSight analyses. The hydrophilic nanogels obtained had a hydrodynamic radius of 78 nm and exhibited a slight positive surface charge. Furthermore, biocompatibility studies using MTS assays revealed that the nanogels demonstrated non-toxic behavior within the investigated concentration range of 0.1 to 400 μg/mL. Additionally, no specific interaction with bovine serum albumin was observed, further indicating their biocompatibility. In summary, 1,6-hexanediol diglycidyl ether, as a cross-linker, enables the fabrication of hydrophilic nanogels with well-controlled properties, such as particle size and surface charge, and ensures their biocompatibility, making them promising candidates for various biomedical applications. 3
Reference
1. 1,6-Hexanediol diglycidyl ether. National Center for Biotechnology Information. 2024; PubChem Compound Summary for CID 85960.
2. Matsumoto Y, Enomoto Y, Kimura S, Iwata T. Highly stretchable curdlan hydrogels and mechanically strong stretched-dried-gel-films obtained by strain-induced crystallization. Carbohydr Polym. 2021; 269: 118312.
3. Legros C, Wirotius AL, De Pauw-Gillet MC, Tam KC, Taton D, Lecommandoux S. Poly(2-oxazoline)-based nanogels as biocompatible pseudopolypeptide nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules. 2015; 16(1): 183-191.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- 1,6-hexanediol diglycidyl ether:Application, Chemistry and Toxic Studies Jan 17, 2023
1,6-hexanediol diglycidyl ether is an ether compound connected to ethylene oxide (oxirane) at both ends. This substance is a colourless and odourless liquid at room temperature and standard atmospheri
Supplementation with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate monohydrate can synthesize neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, maintaining a healthy nervous system.....
Nov 4,2025Biochemical EngineeringAmmonium bicarbonate is a clear white crystalline solid with a faint ammonia smell. It slowly degrades the environment into ammonia, carbon dioxide, and water.....
Apr 9,2024Food Additives1,6-Hexanediol diglycidyl ether
16096-31-4You may like
1,6-Hexanediol diglycidyl ether manufacturers
- 1,6-Hexanediol diglycidyl ether
-

- $0.00 / 1kg
- 2025-12-20
- CAS:16096-31-4
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 98%
- Supply Ability: Customise
- 1,6-Hexanediol diglycidyl ether
-

- $0.00 / 210kg
- 2025-08-22
- CAS:16096-31-4
- Min. Order: 840kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 35 ton/month
- 1,6-Hexanediol diglycidyl ether
-

- $0.00 / 1KG
- 2025-06-27
- CAS:16096-31-4
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 500000kg