The Applications and Safety Considerations of 2-Butene-1,4-diol in Various Industries
Dec 27,2023
General Description
2-Butene-1,4-diol is a versatile chemical compound with a molecular weight of 88.11 g/mol. It has moderate hydrophilicity and exhibits high solubility in water, ethyl alcohol, and acetone. This compound finds applications in various industries, including the production of alkyd resins, plasticizers, nylon, and pharmaceuticals. It serves as a cross-linking agent, comonomer, reducing agent, and fungicide precursor. However, it should be handled with caution as it can be harmful if swallowed and cause skin, eye, and respiratory irritation. Studies on animals have shown its potential to cause convulsions. Precautions must be taken when working with 2-Butene-1,4-diol due to its potentially harmful properties.

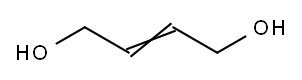
Figure 1. 2-Butene-1,4-diol
Properties and Characteristics
2-Butene-1,4-diol, also known as 2,3-butylene glycol, is a chemical compound with a molecular weight of 88.11 g/mol. It has a computed XLogP3 value of -0.8, indicating a moderate hydrophilicity. The molecule contains two hydrogen bond donor groups and two hydrogen bond acceptor groups. It has two rotatable bonds and a topological polar surface area of 40.5 Ų. Experimentally, 2-Butene-1,4-diol is a nearly colorless and odorless liquid. It may appear faintly yellow-green and has a clear viscous texture. The compound is almost colorless in its liquid form. It has an odorless characteristic. The boiling point of 2-Butene-1,4-diol is in the range of 141-149 °C at 20 mm Hg, while the melting point is 7 °C (45 °F). Its flash point is measured at 128 °C. The compound exhibits high solubility in water, ethyl alcohol, and acetone, while it is sparingly soluble in benzene. The density of 2-Butene-1,4-diol ranges from 1.067 to 1.074. Additional properties include a vapor density of 3.0 (relative to air) and a vapor pressure of 0.04 mmHg. The refractive index of the compound is approximately 1.476-1.478 at 25 °C. It falls into the chemical class of alcohols and polyols. 1
Applications in Various Industries
2-Butene-1,4-diol finds a wide range of applications in various industries. It serves as a valuable chemical intermediate for the production of alkyd resins, plasticizers, nylon, and pharmaceuticals. Alkyd resins are widely used in coatings, adhesives, and paints, while plasticizers enhance the flexibility and durability of plastics. The compound's role in the synthesis of nylon contributes to the manufacturing of fibers, films, and engineering plastics. Furthermore, 2-Butene-1,4-diol is utilized as a cross-linking agent for synthetic resins, which enhances their strength and stability. It is also involved in the production of fungicides, contributing to the control of fungal growth in various agricultural and industrial settings. Additionally, it acts as a comonomer with toluene diisocyanates in the production of polyurethanes, which are used in coatings, foams, adhesives, and sealants. Another application of 2-Butene-1,4-diol is its usage as a reducing agent in chrome tanning baths, which is a process employed in leather tanning and processing. This compound plays a vital role in ensuring proper tanning and improving the quality of leather products. In summary, 2-Butene-1,4-diol demonstrates its versatility as a chemical intermediate in the production of alkyd resins, plasticizers, nylon, and pharmaceuticals. Its applications extend to being a cross-linking agent, comonomer, reducing agent, and fungicide precursor. 2
Toxicity and Precautions
2-Butene-1,4-diol is a chemical compound with various applications. However, it is important to note that this compound can be harmful if swallowed, cause skin irritation, serious eye irritation, and respiratory irritation. In case of emergency, appropriate treatment for irritants should be administered. Studies conducted on rats have shown that 2-Butene-1,4-diol can cause convulsions when administered intraperitoneally. Additionally, it has been identified as an irritant. The LD50 (lethal dose) for oral ingestion in rats is reported to be 1250 mg/kg, while the LD50 for intraperitoneal administration is 327 mg/kg. In mice, the LD50 for intravenous injection is greater than 316 mg/kg. Regarding human toxicity, it has been documented that 2-Butene-1,4-diol can act as a primary skin irritant. However, further information regarding its effects on humans is not provided in the given context. Due to its potentially harmful properties, precautions should be taken when handling or using 2-Butene-1,4-diol. 3
Reference
1. 2-Butene-1,4-diol. National Center for Biotechnology Information, 2023, PubChem Compound Summary for CID 175854.
2. 1,4-Dihydroxy-2-butene. Haz-Map, Information on Hazardous Chemicals and Occupational Diseases, 2820.
3. But-2-ene-1,4-diol. European Chemicals Agency, EC / List no. 203-787-0.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Exploring the Versatility and Safety of 2-Butene-1,4-diol in Industrial Chemistry Apr 26, 2024
2-Butene-1,4-diol exemplifies a key compound in the realm of industrial chemistry with its pivotal role spanning various sectors.
- The synthesis method of 2-Butene-1,4-diol Oct 17, 2023
It is of great value to develop an effective method to synthesize 2-Butene-1,4-diol which is an important organic compound.
Metformin's pharmacokinetics involve active cellular uptake through transporters. Genetic polymorphisms in cation transporters influence its effectiveness and clearance.....
Dec 27,2023APIPoly(methylhydrosiloxane) is a versatile silicone oil used in waterproof coatings, organic synthesis, catalysis, and protective applications in biomedical and electronic fields.....
Dec 27,2023API2-Butene-1,4-diol
110-64-5You may like
2-Butene-1,4-diol manufacturers
- 2-Butene-1,4-diol
-

- $10.00 / 1ASSAYS
- 2024-06-10
- CAS:110-64-5
- Min. Order: 1ASSAYS
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 10 ton
- 2-Butene-1,4-diol
-

- $10.00 / 1kg
- 2024-06-07
- CAS:110-64-5
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99.9%
- Supply Ability: 20ton
- 2-Butene-1,4-diol
-

- $0.00 / 1G
- 2024-06-07
- CAS:110-64-5
- Min. Order: 1G
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 20