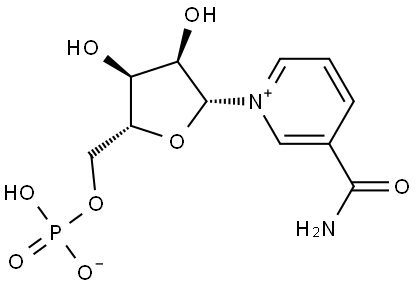
Anti-aging effects and safety of β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide
Nov 15,2023
Introduction of β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide
β-Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is a natural product which exists in small quantity in most plants, such as edamame, broccoli, and cucumber. It is also an endogenous molecule in all mammalian tissues. Its biological functions are linked to the ability to boost nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD), a product of the salvage pathway in NAD biosynthesis in which NMN serves as a precursor. NAD concentration declines with age afecting mammalian longevity and age-related health conditions through its functions of energy metabolization and activations of poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP), Sirtuin proteins, and etc. in mammalian tissues。

Anti-aging effects of NMN
Aging is a major risk factor for many chronic human diseases. In addition, the incidence of many age-related diseases such as hypertension, atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, cancer, Alzheime's disease, as well as many other cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases have risen drastically, leading to a heavy global socioeconomic and medical burden.
Among various antiaging healthcare products, as an antiaging product, nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) has attracted great attention in North America, Europe, and China over the past decade. NMN is used as a dietary supplement and is widely applied in cosmetic products. However, on 10 November, 2022, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) declared that β-NMN is prohibited as a health supplement. FDA concluded that “NMN was authorized for investigation as a new drug (before being lawfully marketed in supplements) and was the subject of substantial clinical investigations that were instituted and made public.” This finding had the effect of excluding NMN as a dietary supplement.
The changes of NAD+ levels during aging
NMN is a main precursor of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), an essential coenzyme for vital cellular physiological activities such as metabolism, cell death, aging, DNA repair, gene expression, and neuroinflammation. As shown in the figure below:

Safety of NMN
Oral NMN does not have any adverse physical effects in healthy men or women. Blood NAD concentrations increased significantly and dose-dependently during NMN treatment. Oral NMN up to 900 mg/day for 60 days was safe and well tolerated. NMN supplementation had a positive effect on physical endurance and general health in healthy adults, as evidenced by significant improvements in the 6-minute walk test, haematobiological age, and SF-36 scores. The 900 mg/day oral dose was not significantly better than the 600 mg/day oral dose.
References:
[1] QIN SONG. The Safety and Antiaging Effects of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide in Human Clinical Trials: an Update.[J]. Advances in nutrition (Bethesda, Md.), 2023. DOI:10.1016/j. advnut. 2023. 08. 008.
[2] LIN YI. The efficacy and safety of β-nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) supplementation in healthy middle-aged adults: a randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, dose-dependent clinical trial.[J]. GeroScience, 2023, 45 1: 29-43. DOI:10.1007/s11357-022-00705-1.
[3] YUICHIRO FUKAMIZU. Safety evaluation of β-nicotinamide mononucleotide oral administration in healthy adult men and women.[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022: 14442. DOI:10.1038/s41598-022-18272-y.
[4] TOMOYO KAWAMURA; K. S; N Mori. β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide, an Anti-Aging Candidate Compound, Is Retained in the Body for Longer than Nicotinamide in Rats.[J]. Journal of nutritional science and vitaminology, 1900, 62 4 1: 272-276. DOI:10.3177/JNSV. 62.272.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Preparation of β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Jan 4, 2024
The one-step conversion of nicotinamide riboside (NR) to β-NMN has been considered to be the most promising synthetic route for β-NMN.
- ANH, NPA ask FDA to reverse position on NMN supplements Aug 7, 2023
FDA has taken the position that NMN does not meet the definition of a dietary ingredient under DSHEA and should be classified as a drug.
- β-nicotinamide mononucleotide: Pharmacodynamics, Functions and Preparation Apr 10, 2023
β-nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is a nucleotide derived from ribose and nicotinamide. It plays an important role in the production of NAD+, which is a coenzyme involved in various biological areas.
Lixisenatide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, improves glycemic control, promotes weight loss, and has cardioprotective properties in type 2 diabetes.....
Nov 15,2023APIElucidating the precise mechanism and role of spermidine in the human aging process will lead to unprecedented health benefits.....
Nov 15,2023APIβ-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide
1094-61-7You may like
β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide manufacturers
- Beta-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide(NMN)
-

- $2.50 / 1g
- 2024-06-09
- CAS:1094-61-7
- Min. Order: 1g
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 1000kg
- β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide
-

- $1.00 / 1kg
- 2024-06-09
- CAS:1094-61-7
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 20 tons
- β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide
-

- $10.00/ kg
- 2024-06-07
- CAS:1094-61-7
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99.99%
- Supply Ability: 10 tons