Applications of potassium peroxymonosulfate
Mar 24,2022
Background
Potassium peroxymonosulfate disinfectants(PMS) is an improvement on chlorine-based disinfectants and cleaning agents. PMS shows a pale red color when dissolved. Since the color tone changes in proportion to the decrease in the effective concentration of the disinfectant, this color change can be useful for estimating the effective concentration without measuring actually it. In this questionnaire survey, the usefulness and utility of PMS at the clinical site ware evaluated. In addition, it was revealed that PMS shows a persistent bactericidal effect for 24 hours for bacteria such as MRSA and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, similar to amphoteric surfactants. Low-level disinfectants such as amphoteric surfactants, chlorhexidine, and quaternary ammonium compounds have been reported to exhibit persistent bactericidal effects.

Picture 1 Potassium peroxymonosulfate disinfectants
Effects of potassium peroxymonosulfate on disintegration of waste sludge
Effects of peroxymonosulfate (PMS) oxidation on disintegration degree (DD) and extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) properties of waste activated sludge were investigated[1]. A combined approach of fractionation procedure and parallel factor (PARAFAC) analysis was applied to characterize EPS of sludge. Results indicated that PMS oxidation effectively broke sludge particles, resulting in DD in total nitrogen of 39.8% at 10 mg PMS / (g SS). After PMS treatment, EPS increased significantly and mostly transferred to slime layer rather than loosely bound EPS (LB-EPS), and the ratio of slime to tightly bound EPS was correlated significantly with PMS dosage. With increasing PMS dosage, polysaccharides in EPS increased, while proteins in EPS and DNA in slime EPS increased firstly and then decreased. PARAFAC analysis of excitation-emission matrix spectra showed that tryptophan-like substances in both slime and LB-EPS were greatly influenced by PMS oxidation, and humic-like fluorophores in slime EPS were positively correlated with PMS dosage.
Chemical and microbial decontamination of pool water using activated potassium peroxymonosulfate
Potassium peroxymonosulfate activation leads to the formation of highly reactive species, mainly the sulfate radicals[2]. Activated potassium peroxymonosulfate (from now on peroxymonosulfate) was tested against specific pollutants such as ammonium ion, creatinine, chlorinated creatinine products, arginine and Escherichia coli (E. coli), all constituents or derivatives of human discharges. The objective was to assess whether activated peroxymonosulfate can be a viable treatment reagent in recreational water applications. It was found that organic molecules such as creatinine, chlorinated creatinine products and arginine could be effectively treated with activated peroxymonosulfate. Ammonium ion was oxidized only by chlorine species and only in de-ionized water. Chlorine species were formed from the reaction of sulfate radicals with chloride ions. In pool water, the reaction of sulfate radicals with chloride ions and the subsequent ammonium ion oxidation were scavenged by the presence of bicarbonate ions. The Co/Peroxymonosulfate system was also shown to be an effective disinfection reagent, since 99.99% (4-log) kill of E. coli was achieved in 60 min of treatment. At the concentrations tested here, however, it is still not efficacious enough to qualify as an EPA-registered sanitizer for swimming pools (requires 6-log kill of E. coli, ATCC 11229, and Enterococcus faecium, ATCC 6569, in 30 s).
Bactericidal efficacy of potassium peroxymonosulfate
Four concentrations of potassium peroxymonosulfate (PPMS) were evaluated for bactericidal activities and indicated that the concentration is less than the manufacturing-recommended concentrations, must extend the exposure time for bacterial inactivation[3]. However, even with and without of organic material contamination, did not show marked inactivation difference. In addition, all concentrations were inactivated on all carrier surfaces within 30 seconds, except on rubber where inactivation occurred within 1 min. However, quaternary ammonium compounds were inactivated on stainless steel and plastic within 1 min and 30 sec, respectively, but not inactivated within 5 min on rubber surfaces. Conclusion, PPMS inactivated bacteria under optimal concentration, organic material conditions, exposure timing and on carrier surfaces which can useful as an alternative disinfectant for biosecurity enhancement.
Evaluation of efficacy and clinical utility of potassium peroxymonosulfate-based disinfectants
Healthcare environments are well known as propagation paths for pathogenic microorganisms[4]. Disinfecting the hands of medical personnel as well as the medical environment, with a focus on frequently touched surfaces, is useful in infection control. As rotavirus (RV) is resistant to alcohol, the use of 200–1,000 ppm Sodium hypochlorite (NaClO) in disinfecting environments contaminated with RV is recommended. NaClO is a disinfectant with a broad antimicrobial spectrum. However, it is problematic for reasons such as corrosion of metal and other equipment surfaces, generation of irritating chlorine gas, and complicated management of concentrations.
On the other hand, disinfectants and cleaning agents formulated with potassium peroxymonosulfate that are improvement over chlorine-based disinfectants and cleaning agents have been reported to be efficacious against many infectious microorganisms such as viruses and bacteria, and they have been used in a manner similar to that of NaClO in the hygiene management of healthcare environments. In addition, it has been reported that with hypochlorous acid as the active substance, there is little metal corrosion and no chlorine odor, and this agent is highly efficacious against many infectious organisms. Furthermore, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) states that potassium peroxymonosulfate-based disinfectants (PPD) are widely effective against such organisms such as norovirus, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), hepatitis B virus, and hepatitis C virus. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) guidelines recommend selection of a disinfectant or cleaning/disinfectant registered with the EPA for use in environmental maintenance. In addition, the Japanese dialysis guidelines recommend the use of potassium peroxymonosulfate in the cleaning and disinfection of environmental surfaces.
Reference
1 Niu T, Zhou Z, Ren W, et al. Effects of potassium peroxymonosulfate on disintegration of waste sludge and properties of extracellular polymeric substances[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2016, 106: 170-177.
2 Anipsitakis G P, Tufano T P, Dionysiou D D. Chemical and microbial decontamination of pool water using activated potassium peroxymonosulfate[J]. Water research, 2008, 42(12): 2899-2910.
3 Kunanusont N, Punyadarsaniya D, Jantafong T, et al. Bactericidal efficacy of potassium peroxymonosulfate under various concentrations, organic material conditions, exposure timing and its application on various surface carriers[J]. Journal of Veterinary Medical Science, 2020: 19-0562.
4 Matsuoka T, Yoshida S, Ohashi K, et al. Evaluation of efficacy and clinical utility of potassium peroxymonosulfate-based disinfectants[J]. Can. J. Infect Control, 2017, 32: 93-97.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
Sitafloxacin (as sitafloxacin hydrate) is available as 50-mg tablets, under the name Gracevit, and as a 10% fine granular preparation. Sitafloxacin inhibits bacterial topoisomerase II (DNA gyrase) and topoisomerase IV and is bactericidal. S....
Mar 23,2022APITrimethoprim, abbreviated as TMP, is an organic compound with chemical formula C14H18N4O3, white or to pale yellow crystalline powder....
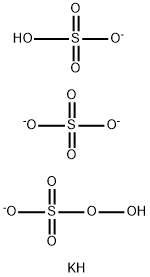
Mar 24,2022APIPOTASSIUM PEROXYMONOSULFATE
37222-66-5You may like
POTASSIUM PEROXYMONOSULFATE manufacturers
- POTASSIUM PEROXYMONOSULFATE
-

- $0.00 / 25KG
- 2023-08-18
- CAS:37222-66-5
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 50000KG/month
- POTASSIUM PEROXYMONOSULFATE
-

- $9.00 / 1KG
- 2023-03-06
- CAS:37222-66-5
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99.8%
- Supply Ability: 100tons
- POTASSIUM PEROXYMONOSULFATE
-

- $10.00 / 1KG
- 2021-09-30
- CAS:37222-66-5
- Min. Order: 100KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 100 mt