窒化ホウ素 化学特性,用途語,生産方法
外観
白色~わずかにうすい褐色, 粉末六方晶の層状構造をもった滑らかな白色の粉末
性質
1. 物理的特性
真空中では1,500℃、不活性雰囲気では2,200℃付近まで、問題無く使用できるほど高い耐熱性があります。また、熱膨張率が小さく熱伝導率がよいため、熱衝撃性に優れています。そういった特性から、窒化ホウ素の成形体は、鋼に近い熱伝導率を有する高熱伝導性のセラミックスとして利用されています。
2. その他の特徴
その他の特徴としては、無機・有機薬品に対して極めて安定であり、優れた耐食性を示します。また、優れた絶縁体でもあり、高周波用の絶縁材料としても活用されています。
定義
本品は、次の化学式で表される無機顔料である。
溶解性
水、エタノール及びアセトンにほとんど溶けない。
解説
プラズマ放電でBNナノチューブが合成され,カーボンナノチューブより高温空気中の安定性が高いため,電子放出用電極材としての開発が進められている.h-BNは無色の結晶.密度2.34 g cm-3.耐熱性が大きいが2500 ℃ 付近から昇華がはじまる.融点約3000 ℃.電気絶縁性は大きい(比抵抗 107 Ω m).耐化学薬品性も大きく,とくに酸に強い.熱アルカリ,溶融炭酸アルカリには急速に侵される.空気中では1100 ℃ 付近までは侵されないが,1200 ℃ 以上では徐々に酸化される.不活性気体中では2000 ℃ 以上まで耐える.水蒸気と加熱すると900 ℃ 以上で分解する.c-BNは無色の結晶.密度3.45 g cm-3.モース硬さ10で,ダイヤモンドにきずをつけることができる.物性および化学性はh-BNに準じる.
森北出版「化学辞典(第2版)
用途
合金の製造。半導体。原子炉。潤滑油。断熱用炉材。るつぼ。化学装置材料。
構造
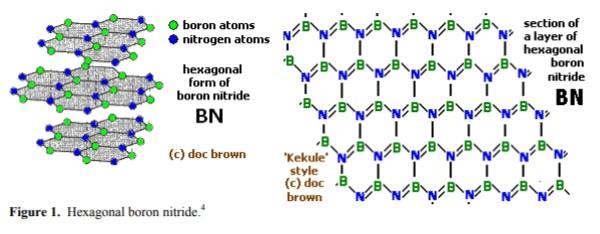
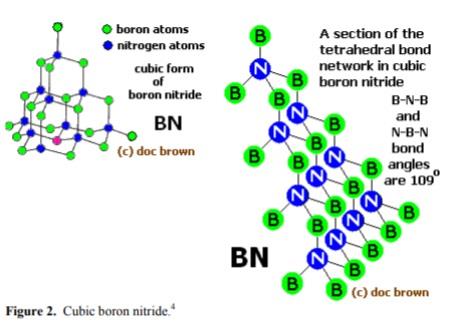
窒化ホウ素,おもな同素体は,六方晶(hexagonal)系のh-BN(α-BN),立方晶(cubic)系のc-BN(β-BN),立方晶系ウルツ鉱型(wurtzite)のw-BN(γ-BN)の3種類.h-BNは,BとNが交互に結合した平面六員環の黒鉛型構造で,平面は層状に重なっている黒鉛と異なり,六員環は各層で,Bの下にN,その下にBがくるように上下に重なっている.B-N1.45 Å.層間距離3.34 Å.
応用
h-BNはバンドギャップ5.8 eV で215 nm の蛍光発光が観測されている.耐熱材(るつぼ),広い温度範囲で使用できる潤滑剤,無機繊維として複合材料などに利用される.c-BNは研磨剤,切削剤(とくにダイヤモンドが使用できない高温用)などに用いられる.p-BNは半導体単結晶製造用るつぼ材料に用いられる.
化粧品の成分用途
滑沢剤、増量剤
製法
ホウ砂とアンモニア,またはホウ砂,ホウ酸またはホウ酸塩とNH4Cl,シアン化アルカリ金属を加熱すると得られる窒化ホウ素.
特長
電気絶縁性を有し化学的、熱的に安定で不活性雰囲気では約3000℃まで安定
説明
Boron nitride is a material in which the extra electron of nitrogen (with respect to carbon) enables it to form structures that are isoelectronic with carbon allotropes.
Boron nitride is an inorganic compound with a flat, hexagonal crystal similar to graphite, but with the carbon atoms replaced by boron and nitrogen atoms. The alternate boron and nitrogen atoms are linked to form interlocking hexagonal rings with three boron atoms and three nitrogen atoms, and the layers are held together by van der Waals forces. There is no boron-nitrogen bonding between the layers.The bond length is 1.466Å and the interlayer spacing is 3.331 Å. A spherical form (with a hexagonal crystal structure) is also available.
Boron nitride can also be in cubic form in which alternately linked boron and nitrogen atoms form a tetrahedral bond network, similar to carbon atoms in diamond.
化学的特性
white powder(s), 1μm or less 99.5% pure; hexagonal, most common form: a=0.2504 nm, c=0.6661nm; fcc: a=0.3615nm; hardness: hexagonal like graphite,?cub approaches that of diamond; band gap ~7.5 eV at 300K; dielectric 7.1; used in furnace insulation and in crucibles for melting aluminum, boron, iron, and silicon, also as sputtering target for dielectrics, diffusion masks, passivation layers [KIR81] [HAW93] [MER06] [CER91]
物理的性質
Insulator (
Eg=7.5 eV). Crucibles
for melting molten metals such
as Na, B, Fe, Ni, Al, Si, Cu, Mg,
Zn, In, Bi, Rb, Cd, Ge, and Sn.
Corroded by molten metals U,
Pt, V, Ce, Be, Mo, Mn, Cr, V, and
Al. Attacked by molten salts
PbO
2, Sb
2O
3, AsO
3, Bi
2O
3, KOH,
and K
2CO
3. Used in furnace
insulation-diffusion masks and
passivation layers.
使用
Boron nitride is a material in which the extra electron of nitrogen (with respect to carbon) enables it to form structures that are isoelectronic with carbon allotropes. Also used in manufacture of alloys; in semiconductors, nuclear reactors, lubricants.
Hexagonal boron nitride can be used as an electrical insulator; as thermocouple protection sheaths, crucibles and linings for reaction vessels; and as a coating for refractory molds used in glass forming and in superplastic forming of titanium. It can also be incorporated in ceramics, alloys, resins, plastics, and rubber to give them self-lubricating properties. Hexagonal boron nitride is used the formulation of coatings and paints for high temperature applications. It is also used as a substrate for semi-conductors, lens coatings, and transparent windows.
https://www.cir-safety.org
調製方法
In tonnage production, acetaldehyde may be manufactured by:
1. The direct oxidation of ethylene, requiring a catalytic solution of copper chloride plus small quantities of palladium chloride Cl2Pd.
2. The oxidation of ethyl alcohol C2H6O with sodium dichromate Cr2Na2O7, and
3. The dry distillation of calcium acetate C4H6CaO4 with calcium formate C2H2CaO4.
定義
boron nitride: A solid, BN, insolublein cold water and slowly decomposedby hot water; r.d. 2.25 (hexagonal);sublimes above 3000°C. Boronnitride is manufactured by heatingboron oxide to 800°C on an acid-solublecarrier, such as calcium phosphate,in the presence of nitrogen orammonia. It is isoelectronic with carbonand, like carbon, it has a veryhard cubic form (borazon) and asofter hexagonal form; unlikegraphite this is a nonconductor. It isused in the electrical industrieswhere its high thermal conductivityand high resistance are of especialvalue.
主な応用
Boron nitride finds applications in shaping tools in industries due to its ability to withstand temperatures greater than 2,000°C. Cutting tools and abrasive components, designed specifically for use with low-carbon ferrous metals, have been developed using cubic boron nitride. These tools perform similarly to polycrystalline diamond (PCD) tools but can be utilized on iron and low-carbon alloys without the risk of a reaction occurring.
製造方法
Boron nitride is prepared by heating boric oxide with ammonia:
B
2O
3 + 2NH
3 → 2BN + 3H
2O
Alternatively, the compound can be prepared by heating boric oxide or boric acid with ammonium chloride or an alkali metal cyanide. Purified product can be obtained by high temperature reaction of boron halide with ammonia:
BCl
3 + NH
3 → BN + 3HCl
Boron nitride can also be made from the elements by heating boron and nitrogen at red heat.
一般的な説明
Boron nitride in cubic form, known as Borazon, is a manufactured abrasive that was discovered by General Electric Co. Laboratories in 1957. Unlike manufactured diamond, Borazon does not have a natural counterpart. It is produced under temperatures and pressures similar to those required for diamond manufacture. Additionally, cubic boron nitride exhibits greater thermal stability compared to diamond. It remains stable at temperatures exceeding 1,371°C, while diamond reverts to graphite at temperatures above 816°C. Borazon has a Knoop hardness (K100) of 7800, which is higher than ordinary abrasives but lower than diamond.
法規情報
窒化ホウ素は毒物及び劇物取締法や消防法で、特に指定されていません。化学物質排出把握管理促進法 (PRTR法) では、第1種指定化学物質 (法第2条第2項、施行令第1条別表第1、第1種管理No. 405) に指定されています。
使用用途
窒化ホウ素は、熱伝導性や電気絶縁性に優れていることから、放熱樹脂シートや放熱基板用のフィラーとして幅広く使用されます。
耐熱性や耐食性、潤滑・離型性にも優れた材料であるため、各種マトリックスへの添加材としても使用されています。具体的な用途の例として、各種放熱材料の添加材、、オイル添加材、高温潤滑添加材等が挙げられます。また、各種金属・の耐熱離型材や溶融金属保護コーティング材等としても使用されております。
感触改良やを目的として、メイクアップ化粧品や日焼け止め製品等にも、窒化ホウ素が使用されることもあります。
処理と保存
取扱い及び保管上の注意は、下記の通りです。
- 容器を密栓し、乾燥した冷暗所に保管する。
- 屋外や換気の良い区域のみで使用する。
- 強酸化剤との接触は避ける。
- 使用時は保護手袋、保護眼鏡を着用する。
- 取扱い後はよく手を洗浄する。
- 皮膚に付着した場合は、石鹸と水で洗い流す。
- 眼に入った場合は、水で数分間注意深く洗う。
参考文献
工業用途
Boron nitride (BN) has many potential commercial applications. It is a white, fluffy powder with a greasy feel. It is used for heat-resistant parts by molding and pressing the powder without a binder to a specific gravity of 2.1 to 2.25.
BN may be prepared in a variety of ways, for example, by the reaction of boron oxide with ammonia, alkali cyanides, and ammonium chloride, or of boron halides and ammonia. The usually high chemical and thermal stability, combined with the high electrical resistance of BN, suggests numerous uses for this compound in the field of high-temperature technology. BN can be hot-pressed into molds and worked into desired shapes.
BN powders can be used as mold-release agents, high-temperature lubricants, and additives in oils, rubbers, and epoxies to improve thermal conductance of dielectric compounds. Powders also are used in metal- and ceramicmatrix composites (MMC and CMC) to improve thermal shock and to modify wetting characteristics.
The platy habit of the particles and the fact that boron nitride is not wet by glass favors use of the powder as a mold wash, e.g., in the fabrication of high-tension insulators. It is also useful as thermal insulation in induction heating. A cubic form of boron nitride (Borazon) similar to diamond in hardness and structure has been synthesized by the high-temperature, high-pressure process for making synthetic diamonds. Any uses it may find as a substitute for diamonds will depend on its greatly superior oxidation resistance.
工業用途
The major industrial applications of hexagonal boron nitride rely on its high thermal conductivity, excellent dielectric properties, self-lubrication, chemical inertness, nontoxicity, and
ease of machining. These are, for instance, mold wash for releasing molds, high-temperature
lubricants, insulating filler material in composite materials, as an additive in silicone oils and
synthetic resins, as filler for tubular heaters, and in neutron absorbers. On the other hand, the
industrial applications of cubic boron nitride rely on its high hardness and are mainly as
abrasives.
Forms and nomenclature
Boron nitride exists as three different poly-morphs:
Alpha-boron nitride (α-BN), a soft and ductile polymorph (ρ = 2280 kg.m
–3 and m.p. = 2700°C) with a hexagonal crystal lattice similar to that of graphite, also called hexagonal boron nitride
(HBN) or white graphite;
Beta-boron nitride (β-BN), the hardest manmade material and densest polymorph (ρ = 3480 kg.m
–3, m.p. = 3027°C), with a cubic crystal lattice similar to that of
diamond, also called cubic boron nitride (CBN) or borazon;
Pyrolitic boron nitride
(PBN). From a chemical point of view, boron nitride oxidizes readily in air at temperatures
above 1100°C, forming a thing protective layer of boric acid (H
3BO
3) on its surface that prevents further oxidation as long as it coats the material. Boron nitride is stable in reducing
atmospheres up to 1500°C.
窒化ホウ素 上流と下流の製品情報
原材料
準備製品