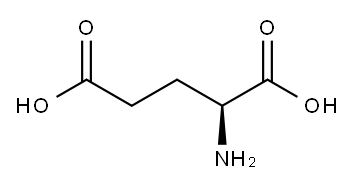
L-글루타민산
|
|
L-글루타민산 속성
- 녹는점
- 205 °C (dec.) (lit.)
- 끓는 점
- 267.21°C (rough estimate)
- 알파
- 32 º (c=10,2N HCl)
- 밀도
- 1.54 g/cm3 at 20 °C
- 굴절률
- 1.4300 (estimate)
- 저장 조건
- 2-8°C
- 용해도
- 1M HCl: 100mg/mL
- 물리적 상태
- 가루
- 산도 계수 (pKa)
- 2.13(at 25℃)
- 색상
- 하얀색
- 수소이온지수(pH)
- 3.0-3.5 (8.6g/l, H2O, 25℃)
- 냄새
- 100.00%에서. 순한 효모로 구운 빵
- ?? ??
- 효모
- optical activity
- [α]20/D +32°, c = 10 in 2 M HCl
- 수용성
- 7.5g/L(20℃)
- 최대 파장(λmax)
- λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.1
λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.1
- JECFA Number
- 1420
- Merck
- 14,4469
- BRN
- 1723801
- InChIKey
- WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-VKHMYHEASA-N
- LogP
- -3.69
- CAS 데이터베이스
- 56-86-0(CAS DataBase Reference)
- 위험 및 안전 성명
- 위험 및 사전주의 사항 (GHS)
| 위험품 표기 | Xi | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 위험 카페고리 넘버 | 36/37/38 | ||
| 안전지침서 | 24/25-36-26 | ||
| WGK 독일 | 2 | ||
| RTECS 번호 | LZ9700000 | ||
| F 고인화성물질 | 10 | ||
| TSCA | Yes | ||
| HS 번호 | 29224200 | ||
| 유해 물질 데이터 | 56-86-0(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| 독성 | LD50 orally in Rabbit: > 30000 mg/kg | ||
| 기존화학 물질 | KE-01563 |
L-글루타민산 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
물성
무색~백색의 주상결정 또는 백색의 결정성분말로서 냄새는 없으나 특이한 맛을 가지고 있다. 화학식은 C5H8NNaO4·H2O이다. 물에는 잘 녹고, 알코올에는 약간 녹으며 에테르에는 녹지 않는다. 빛이나 열에 안정하다.용도
글루탐산 나트륨(영어: sodium glutamate) 또는 글루탐산 일나트륨(영어: monosodium glutamate, MSG)은 가장 풍부한 자연발생 불필수 아미노산인 글루탐산의 나트륨염이다.순도시험
(1) 비선광도 : 이 품목을 미리 건조한 다음 10g을 정밀히 달아 2N 염산에 녹여 100mL로 하여 이 액의 선광도를 측정할 때, 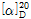 =+31.5~+32.2°이어야 한다.
=+31.5~+32.2°이어야 한다.
(2) 납 : 이 품목 5.0g을 취하여 원자흡광광도법 또는 유도결합플라즈마발광광도법에 따라 시험할 때, 그 양은 1.0ppm 이하이어야 한다.
(3) 비소 : 이 품목을 비소시험법에 따라 시험할 때, 그 양은 4.0ppm 이하이어야 한다.
(4) 피롤리돈카복실산 : 이 품목 1g을 달아 물 100mL에 녹인 액을 시 험용액으로 한다. 따로, 피롤리돈카복실산(pyrrolidone carboxylic acid) 1g을 달아 물에 녹인 액을 대조액으로 한다. 시험용액 및 대조액 1μL 씩을 미리 박층크로마토그래피용 실리카겔을 사용하여 조제한 박층판 에 점적한 후 n-부탄올․빙초산․물의 혼액(2 : 1 : 1)을 전개용매로 하여 약 10cm 전개하고 박층판을 80℃에서 30분간 건조시킨다. 이에 발색시액을 분무하고 80℃에서 10분간 가열하여 발색된 반점을 관찰 할 때, 시험용액에서는 대조액과 같은 위치에 피롤리돈카복실산 반점 이 나타나서는 아니 된다.
발색시액 : 닌히드린 1g 및 초산 3mL에 n-부탄올을 가하여 100mL로 한다.
확인시험
(1) 이 품목 0.15g을 물 4mL 및 수산화나트륨시액 1mL 혼액에 녹이고 닌히드린용액(0.2→100) 1mL 및 초산나트륨 0.1g을 가하고 수욕조에서 10분간 가열할 때, 진한 청자색을 나타낸다.
(2) 이 품목 1g을 물 9mL에 녹인 현탁액에 1N 염산 5.6mL 또는 1N 수산화나트륨용액 6.8mL를 가하여 이 액을 저으면 완전히 녹는다.
정량법
「L-글루탐산나트륨」의 정량법에 따라 정량한다.
0.1N 과염소산용액 1mL = 14.71mg C5H9NO4
강열잔류물
이 품목의 강열잔류물은 0.2% 이하이어야 한다.
개요
L-Glutamic acid, or L-2-aminopentanedioic acid, is a naturally occurring amino acid of plant and animal proteins. It has a very faint odor reminiscent of yeast or freshly baked bread. It has a mild, somewhat sweet, meat-like taste.The average glutamic acid content of food proteins is 20 percent. Expressed as glutamic acid per 100 g of the edible portions, medium fat beef contains about 2.65 g of glutamic acid; whole liquid cow milk, 0.82 g; lean pork, 2.16 g; haddock, 2.32 g; peas, 5.58 g; soybeans, 7.01 g; commeal, 1.62 g; and whole grain wheat flour, 4.16 g. In addition, free glutamic acid is present in many vegetables, fish, and meats in small amounts (0. 005 to 0.23 g per 100 g) and as high as 2 g per 100 g in some varieties of cheese. Recent estimates of free amino acids in the milk of various species indicated that the free glutamic acid in human milk is about 0.22 g per 100 mL.
Glutamic acid and its salts are prepared commercially by hydrolysis of gluten (wheat, corn, soybean, sugarbeet protein); by fermentation from glucose-containing raw materials; the racemic acid may be resolved into the d- and ι-isomer by fractional crystallization; from 2 -cyclopentenylamine; by microbial conversion of aketoglutaric acid; or by an alternative method, using Bacillus megatherium-cereus; from fumaric acid using B. pumilus; from starch.
Glutamic acid and the hydrochloride as well as the mono-sodium, -potassium, and -ammonium salts of L-glutamic acid share similar physical properties: they are nearly odorless, white, free-flowing crystalline powders, and except for glutamic acid and glutamic acid hydrochloride, are freely soluble in water. Glutamic acid is slightly soluble and glutamic acid hydrochloride moderately soluble in water. The pH of a saturated solution is about 3.2.
화학적 성질
L-Glutamic acid has a very faint odor reminiscent of yeast or freshly baked bread and a mild, somewhat sweet, meat- like taste This is a naturally occurring amino acid of plant and animal proteins The average glutamic acid content of food proteins is 20%, expressed as glutamic acid per 100 g of the edible portions For a detailed description, see Burdock (1997).출처
Reported as occurring in many vegetable proteins, in beef fbrin, in the chrysalis of silkworm, in the hydro- lysate of crystalline insulin Also present in other important peptides, such as glutathione, tyrocidin, folic acid, β-lactoglobulin, secretin and bacitracin, and in growth hormone용도
L-glutamic acid or its salt, monosodium glutamate (MSG), is used as an additive to human food to enhance the taste. Although seaweed had been used in Asia to enhance food flavor for over 1000 years, it was not until 1908 that the essential component responsible for the flavor phenomenon was identified as glutamic acid. From 1910 until 1956, monosodium glutamate was extracted from sea weed, a slow and costly method. In 1956, Ajinomoto, a Japanese company, succeeded in producing glutamic acid by means of fermentation. Today, L-glutamic acid or MSG is generally made by microbial fermentation using genetically modified bacteria.정의
ChEBI: An optically active form of glutamic acid having L-configuration.제조 방법
By hydrolysis of gluten (wheat, corn or other vegetable sources); by fermentation from glucose-containing raw materials; the racemic acid may be resolved into the d- and l-isomer by fractional crystallization; from 2-cyclopentenylamine; by microbial conversion of α-ketoglutaric acid; or by an alternative method, using Bacillus megatherium-cereus; from fumaric acid, using B pumilus; from starch.생명 공학 생산
For industrial production of L-glutamic acid, molasses (sucrose), starch hydrolysates (glucose) and ammonium sulfate are generally used as carbon and nitrogen sources, respectively. Key factors in controlling the fermentation are the presence of biotin in optimal concentration – to optimize cell growth and the excretion of Lglutamate – and sufficient supply of oxygen to reduce the accumulation of byproducts, such as lactic and succinic acid. In biotin-rich fermentation media the addition of penicillin or cephalosporin C favors the overproduction of L-glutamic acid due to effects on the cell membrane. The supplementation of fatty acids also results in an increased permeability of the cells thus enhancing glutamate excretion.A strain of Microbacterium ammoniaphilum cultured under biotin-deficient conditions produced 58 % of L-glutamic acid formed from glucose via phosphoenolpyruvate, citrate, and of a-ketoglutarate and the other 42 % via the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) or the glyoxylate cycle.
생물학적 활성
The predominant excitatory transmitter in the mammalian central nervous system. Acts at ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptors.Safety Profile
Human systemic effects by ingestion and intravenous routes: headache and nausea or vomiting. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.Purification Methods
Crystallise L-glutamic acid from H2O acidified to pH 3.2 by adding 4volumes of EtOH, and drying at 110o. Likely impurities are aspartic acid and cysteine. It sublimes at 170-175o/10mm. It melts at 160o with cyclisation to L-pyrrolidone carboxylic acid. [Dunn & Brophy J Biol Chem 99 224 1958, Parikh et al. J Am Chem Soc 80 9571958, Greenstein & Winitz The Chemistry of the Amino Acids J. Wiley, Vol 3 pp 1929-1952 1961, Beilstein 4 III 1530, 4 IV 3028.]L-글루타민산 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
준비 용품
L-글루타민산 공급 업체
| 공급자 | 전화 | 이메일 | 국가 | 제품 수 | 이점 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wuhan Quanjinci New Material Co.,Ltd. | +8615271838296 |
kyra@quanjinci.com | China | 1534 | 58 |
| Hebei Yanxi Chemical Co., Ltd. | +8617531190177 |
peter@yan-xi.com | China | 6000 | 58 |
| Shanghai UCHEM Inc. | +862156762820 +86-13564624040 |
sales@myuchem.com | China | 6709 | 58 |
| Sinoway Industrial co., ltd. | 0592-5800732; +8613806035118 |
xie@china-sinoway.com | China | 992 | 58 |
| Anhui Ruihan Technology Co., Ltd | +8617756083858 |
daisy@anhuiruihan.com | China | 994 | 58 |
| Shandong Juchuang Chemical Co., LTD | +undefined15030412209 |
admin@juchuangchem.com | China | 387 | 58 |
| Shaanxi TNJONE Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd | +8618740459177 |
sarah@tnjone.com | China | 1125 | 58 |
| Ouhuang Engineering Materials (Hubei) Co., Ltd | +8617702722807 |
admin@hbouhuang.com | China | 3001 | 58 |
| Hebei Zhuanglai Chemical Trading Co.,Ltd | +8613343047651 |
admin@zlchemi.com | China | 1770 | 58 |
| Hebei Shengyang Water Conservancy Engineering Co., Ltd. | +8615373025980 |
clara@hbshengyang.com | China | 783 | 58 |