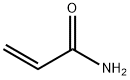
아크릴아마이드
|
|
아크릴아마이드 속성
- 녹는점
- 82-86 °C(lit.)
- 끓는 점
- 125 °C25 mm Hg(lit.)
- 밀도
- 1,322 g/cm3
- 증기 밀도
- 2.45 (vs air)
- 증기압
- 0.03 mm Hg ( 40 °C)
- 굴절률
- 1.460
- 인화점
- 138 °C
- 저장 조건
- 2-8°C
- 용해도
- 2040g/L(25°C)
- 산도 계수 (pKa)
- 15.35±0.50(Predicted)
- 물리적 상태
- 가루
- 색상
- 하얀색
- 냄새
- 무취 고체
- 수소이온지수(pH)
- 5.0-7.0 (50g/l, H2O, 20℃)
- 수용성
- 아크릴아미드는 물에서 250mg/mL로 정기적으로 테스트되어 투명한 무색 용액을 제공합니다. 물에 최소 40%(w/v) 용해되며, 30°C에서 물에 최대 215g/100mL까지 용해되는 것으로 알려졌습니다.
- 감도
- Light Sensitive
- Merck
- 14,129
- BRN
- 605349
- Henry's Law Constant
- (x 10-9 atm?m3/mol): 3.03 at 20 °C (approximate - calculated from water solubility and vapor pressure)
- 노출 한도
- Potential occupational carcinogen. NIOSH REL: TWA 0.03, IDLH: 60; OSHA PEL: TWA 0.3; ACGIH TLV: TWA 0.03.
- 안정성
- 불안정한. 50C 이상으로 가열하지 마십시오. 폭발물. 산, 염기, 산화제, 환원제, 철 및 철염, 구리, 알루미늄, 황동, 자유 라디칼 개시제와 호환되지 않습니다. 공기에 민감합니다. 흡습성.
- InChIKey
- HRPVXLWXLXDGHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
- LogP
- -0.9 at 20℃ and pH7
- CAS 데이터베이스
- 79-06-1(CAS DataBase Reference)
- IARC
- 2A (Vol. 60, Sup 7) 1994
- NIST
- Acrylamide(79-06-1)
- 위험 및 안전 성명
- 위험 및 사전주의 사항 (GHS)
| 위험품 표기 | T | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 위험 카페고리 넘버 | 45-46-20/21-25-36/38-43-48/23/24/25-62-48/20/21/22-22-24/25 | ||
| 안전지침서 | 53-45-24-36/37/39-26-36/37 | ||
| 유엔번호(UN No.) | UN 3426 6.1/PG 3 | ||
| WGK 독일 | 3 | ||
| RTECS 번호 | AS3325000 | ||
| F 고인화성물질 | 8-10 | ||
| TSCA | Yes | ||
| 위험 등급 | 6.1 | ||
| 포장분류 | III | ||
| HS 번호 | 29241900 | ||
| 유해 물질 데이터 | 79-06-1(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| 독성 | LD50 i.p. in mice: 170 mg/kg (Peterson, Sheth) | ||
| IDLA | 60 mg/m3 | ||
| 기존화학 물질 | KE-29374 | ||
| 유해화학물질 필터링 | 97-1-171 | ||
| 중점관리물질 필터링 | 별표1-25 | ||
| 함량 및 규제정보 | 물질구분: 유독물질; 혼합물(제품)함량정보: 아크릴아미드 및 이를 0.1% 이상 함유한 혼합물 |
아크릴아마이드 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
물성
아크릴아마이드는 아크릴로니트릴(acrylonitrile)로부터 합성되는 비닐단량체로 분자량 71.08의 백색, 무취의 결정성 고체이다.용도
주로 화학적·산업적 용도에 널리 사용되는데 정수 시설이나 폐수 처리 시설의 응집제, 종이강화제, 화장품의 피부연화제, 윤활제, 거품생성 보조제, 실험용 크로마토그래피의 폴리아크릴아마이드 겔등으로 사용된다.개요
Acrylamide is an odorless, white crystalline solid that initially was produced for commercial purposes by reaction of acrylonitrile with hydrated sulfuric acid.Acrylamide exists in two forms: a monomer and a polymer. Monomer acrylamide readily participates in radicalinitiated polymerization reactions, whose products form the basis of most of its industrial applications. The single unit form of acrylamide is toxic to the nervous system, a carcinogen in laboratory animals and a suspected carcinogen in humans. The multiple unit or polymeric form is not known to be toxic.
Acrylamide is formed as a by-product of the Maillard reaction. The Maillard reaction is best known as a reaction that produces pleasant flavor, taste, and golden color in fried and baked foods; the reaction occurs between amines and carbonyl compounds, particularly reducing sugars and the amino acid asparagine. In the first step of the reaction, asparagine reacts with a reducing sugar, forming a Schiff’s base. From this compound, acrylamide is formed following a complex reaction pathway that includes decarboxylation and a multistage elimination reaction. Acrylamide formation in bakery products, investigated in a model system, showed that free asparagine was a limiting factor. Treatment of flours with asparaginase practically prevented acrylamide formation. Coffee drinking and smoking are other major sources apart from the human diet.
화학적 성질
Acrylamide, in monomeric form, is an odorless, flake-like crystals which sublime slow at room temperature. May be dissolved in a flammable liquid.용도
Over 90% of acrylamide is used to make polyacrylamides (PAMs), and the remaining 10% is used to make N-methylolacrylamide (NMA) and other monomers. Water treatment PAMs consumed 60% of the acrylamide; PAMs for pulp and paper production consume 20% of the acrylamide; and PAMs for mineral processing consume 10% of the acrylamide. Some of the specific uses of acrylamide are:
In liquid-solid separation where acrylamide polymers act as flocculants and aids in mineral processing, waste treatment and water treatment. They also help reduce sludge volumes in these applications.
As additives in the manufacture of paper and paper board products, leather and paint industries. In the paper industry PAMs act as retention aids during wet end processing and in wet strength additives.
In the manufacture of synthetic resins for pigment binders for textile/leather industries, and In enhanced oil recovery.
use in protein electrophoresis (PAGE), synthesis of dyes and copolymers for contact lenses. It is reasonably anticipated to be a hum an carcinogen.
정의
ChEBI: A member of the class of acrylamides that results from the formal condensation of acrylic acid with ammonia.제조 방법
The principal synthetic route to making acrylamide involves the hydration of acrylonitrile (ACRN). In this process an aqueous ACRN solution reacts over a copper-oxide-chromium oxide catalyst at approximately 100°C. Several other catalyst systems have been used, and most of them contain copper - in some form. The reaction step is followed by purification and concentration to a 50% solution in a vacuum evaporator. The yield of acrylamide from ACRN is 98%. The purification and concentration steps are costly and also involve the recycle of ACRN back to the reaction step. In the early part of the new century, a catalytic distillation process has been developed that converts almost 100% of the ACRN to acrylamide and allows concentration to occur in the same column where acrylamide is made. Therefore this process is less costly.Nitto Chemical (now Dia-Nitrix) introduced a biosynthetic route from ACRN to acrylamide in Japan in 1985. This process uses an immobilized nitrile hydratase biocatalyst that converts the ACRN solution to acrylamide with a yield of 99.5%. This high yield allows a concentrated acrylamide solution to be made without the need for ACRN recycle or solution concentration. This process therefore has lower energy costs.
일반 설명
A solution of a colorless crystalline solid. Flash point depends on the solvent but below 141°F. Less dense than water. Vapors heavier than air. Toxic oxides of nitrogen produced during combustion. Used for sewage and waste treatment, to make dyes and adhesives.공기와 물의 반응
Acrylamide is very soluble in water. The solvent is not necessarily water soluble.반응 프로필
ACRYLAMIDE SOLUTION reacts with azo and diazo compounds to generate toxic gases. Flammable gases are formed with strong reducing agents. Combustion generates mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx). Spontaneous, violent polymerization occurs at the melting point (86°C of the undissolved solid [Bretherick, 5th ed., 1995, p. 428].건강위험
The acute toxicity of acrylamide is moderate by ingestion or skin contact. Skin exposure leads to redness and peeling of the skin of the palms. Aqueous acrylamide solutions cause eye irritation; exposure to a 50% solution of acrylamide caused slight corneal injury and slight conjunctival irritation, which healed in 8 days. The chronic toxicity of acrylamide is high. Repeated exposure to ~2 mg/kg per day may result in neurotoxic effects, including unsteadiness, muscle weakness, and numbness in the feet (leading to paralysis of the legs), numbness in the hands, slurred speech, vertigo, and fatigue. Exposure to slightly higher repeated doses in animal studies has induced multisite cancers and reproductive effects, including abortion, reduced fertility, and mutagenicity. Acrylamide is listed in IARC Group 2B ("possible human carcinogen") and is classified as a "select carcinogen" under the criteria of the OSHA Laboratory Standard.인화성 및 폭발성
The volatility of acrylamide is low (0.03 mmHg at 40 °C), and it does not pose a significant flammability hazard.화학 반응
Reactivity with Water No reaction; Reactivity with Common Materials: Data not available; Stability During Transport: Stable; Neutralizing Agents for Acids and Caustics: Not pertinent; Polymerization: May occur at temperature above 50°C (120°F); Inhibitor of Polymerization: Oxygen (air) plus 50 ppm of copper as copper sulfate.색상 색인 번호
Acrylamide is used in the plastic polymers industry for water treatments and soil stabilization and to prepare polyacrylamide gels for electrophoresis. This neurotoxic, carcinogenic, and genotoxic substance is known to have caused contact dermatitis in industrial and laboratory workersSafety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic and neoplastigenic data. Poison by ingestion, skin contact, and intraperitoneal routes. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. A skin and eye irritantIntoxication from it has caused a peripheral neuropathy, erythema, and peeling palms. In industry, intoxication is mainly via dermal route, next via inhalation, and last via ingestion. Time of onset varied from 1-24 months to 8 years. Symptoms were, via dermal route, a numbness, tingling, and touch tenderness. In a couple of weeks, coldness of extremities; later, excessive sweating, bluish-red and peeling palms, marked fatigue and limb weakness. It is dangerous because it can be absorbed through the unbroken skin. From animal experiments it seems to be a central nervous system toxin. Adult rats fed an average of 30 mg/kg for 14 days were all partially paralyzed and had reduced their food consumption by 50 percent. Polymerizes violently at its melting point. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid fumes and NOX,.잠재적 노출
Added to water during sewage/wastewater treatment. Used in the manufacture of plastics, resins, rubber, synthetic textiles; as a dye, pigment. A major application for monomeric acrylamide is in the production of polymers as polyacrylamides. Polyacrylamides are used for soil stabilization, gel chromatography, electrophoresis, papermaking strengtheners, clarifications, and treatment of potable water and foods.Carcinogenicity
Acrylamide is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in experimental animals.환경귀착
Biological. Bridié et al. (1979) reported BOD and COD values of 0.05 and 1.33 g/g using filtered effluent from a biological sanitary waste treatment plant. These values were determined using a standard dilution method at 20 °C for a period of 5 d. When a sewage seed was used in a separate screening test, a BOD value of 0.92 g/g was obtained. In a treatment plant, a BOD value of 0.40 g/g was reported after 10 d (Mills et al., 1953). The ThOD for acrylamide is 1.35 g/g.Soil. Under aerobic conditions, acrylamide degraded to ammonium ions which oxidized to nitrite ions and nitrate ions. The ammonium ions produced in soil may volatilize as ammonia or accumulate as nitrite ions in sandy or calcareous soils (Abdelmagid and Tabatabai, 1982).
Chemical/Physical. Readily polymerizes at the melting point or under UV light. In the presence of alkali, polymerization is a violent reaction. On standing, may turn to yellowish color (Windholz et al., 1983).
저장
In particular, this substance should be handled only when wearing appropriate impermeable gloves to prevent skin contact, and all operations that have the potential of producing acrylamide dusts or aerosols of solutions should be conducted in a fume hood to prevent exposure by inhalation.운송 방법
UN2074 Acrylamide, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materialsPurification Methods
Crystallise acrylamide from acetone, chloroform, ethyl acetate, methanol or *benzene/chloroform mixture, then vacuum dry and store it in the dark under vacuum. Recrystallise it from CHCl3 by dissolving 200g in 1L, heating to boiling and filtering without suction in a warmed funnel through Whatman 541 filter paper; allowing to cool to room temperature and keeping at -15o overnight. The crystals are collected with suction in a cooled funnel and washed with 300mL of cold MeOH. The crystals are air-dried in a warm oven. [Dawson et al. Data for Biochemical Research, Oxford Press 1986 p. 449, Beilstein 2 IV 1471.] CAUTION: Acrylamide is extremely TOXIC (neurotoxic), and precautions must be taken to avoid skin contact or inhalation. Use gloves and handle in a well-ventilated fume cupboard.비 호환성
Acrylamide may decompose with heat and polymerize at temperatures above 84 C, or exposure to light, releasing ammonia gas. Reacts violently with strong oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Reacts with reducing agents; peroxides, acids, bases, and vinyl polymerization initiators. Fine particles of dust form explosive mixture with air.폐기물 처리
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. Acrylamide residue and sorbent material may be packaged in epoxy-lined drums and taken to an EPAapproved disposal site. Incineration with provisions for scrubbing of nitrogen oxides from flue gases. Deep well injection.아크릴아마이드 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
준비 용품
아크릴아마이드 공급 업체
| 공급자 | 전화 | 이메일 | 국가 | 제품 수 | 이점 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tianjin Zhongxin Chemtech Co., Ltd. | +86-022-66880623 +8618622897568 |
sales@tjzxchem.com | China | 559 | 58 |
| Capot Chemical Co.,Ltd. | 571-85586718 +8613336195806 |
sales@capotchem.com | China | 29797 | 60 |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 |
info@tianfuchem.com | China | 21689 | 55 |
| Shanghai Time Chemicals CO., Ltd. | +86-021-57951555 +8617317452075 |
jack.li@time-chemicals.com | China | 1807 | 55 |
| Hangzhou FandaChem Co.,Ltd. | 008657128800458; +8615858145714 |
fandachem@gmail.com | China | 9341 | 55 |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | +86-0551-65418679 +86-18949832763 |
info@tnjchem.com | China | 2989 | 55 |
| Hubei Jusheng Technology Co.,Ltd. | 18871490254 |
linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 28180 | 58 |
| Yunbio Tech Co.,Ltd. | +86-010-60605551 +86-18046518538 |
yunbiochem@126.com | China | 321 | 58 |
| Hubei xin bonus chemical co. LTD | 86-13657291602 |
linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 22968 | 58 |
| Shandong chuangyingchemical Co., Ltd. | 18853181302 |
sale@chuangyingchem.com | CHINA | 5909 | 58 |