| Company Name: |
Triveni chemicals
|
| Tel: |
08048762458 |
| Email: |
sales@trivenichemical.com |
| Products Intro: |
Product Name:Lead Arsenate
CAS:7784-40-9
|
| Company Name: |
Otto Chemie Pvt. Ltd.
|
| Tel: |
+91 9820041841 |
| Email: |
info@ottokemi.com |
| Products Intro: |
Product Name:Lead arsenate
CAS:7784-40-9
|
|
| | LEAD ARSENATE Basic information |
| Product Name: | LEAD ARSENATE | | Synonyms: | acidleadarsenate;acidleadorthoarsenate;arsenateoflead;arsenicacid(h3aso4),lead(2+)salt(1:1);arsenicacid(h3aso4),lead(2++)salt(1:1);LEAD ARSENATE;arsenicacid,lead(2+)salt(1:1);Arsenicacidlead(2+)salt(1:1) | | CAS: | 7784-40-9 | | MF: | AsHO4Pb | | MW: | 347.13 | | EINECS: | 232-064-2 | | Product Categories: | | | Mol File: | 7784-40-9.mol | 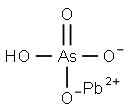 |
| | LEAD ARSENATE Chemical Properties |
| Melting point | decomposes at 1042℃ [HAW93] | | density | 5.79 | | solubility | insoluble in H2O; soluble in HNO, alkaline solutions 3 | | form | white monoclinic crystals | | color | white monoclinic crystals, crystalline | | Water Solubility | insoluble H2O; soluble HNO3, alk [CRC10] | | Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) | pKsp: 35.39 | | CAS DataBase Reference | 7784-40-9 | | EPA Substance Registry System | Lead(II) arsenate (1:1) (7784-40-9) |
| | LEAD ARSENATE Usage And Synthesis |
| Description | Lead arsenate appears as odourless white heavy powder and practically is insoluble in water. It is not combustible and emits irritating or toxic fumes (or gases) in a fire. Lead arsenate is currently used as a growth regulator on grape fruit crop. A large bulk of lead arsenate is also used annually to control cockroaches, silverfish, crickets, earthworms, and other soil-inhabiting insects on golf greens and lawns and on airport turf adjoining runways to reduce bird hazard related to earthworm. Lead arsenate is quite stable and readily accumulates in soils either as a result of use in specific soil treatments or foliar application. Lead arsenate insecticide was used in many countries, including Australia, Canada, New Zealand, and the United States. It was used for insect pests on apples and other fruit tree, garden crops and turf grasses, on rubber and coffee trees, and for mosquito abatement in cattle dips. All insecticidal uses of lead arsenate in the United States were officially banned on August 1, 1988 (U.S. EPA, 1988), with a comment that all registrations for insecticidal use had lapsed before that date. In Australia, use of lead arsenate decreased after the introduction of DDT in 1950, and it has not been used on exported crops since 1983. | | Chemical Properties | Lead arsenate is an odorless, white, heavy powder. It is not combustible and emits irritating
or toxic fumes (or gases) in a fi re. Lead arsenate enters the body by inhalation, or from
contaminated food and beverages. It is used to make insecticides. | | Chemical Properties | Lead arsenate is an odorless, heavy, white
powder, or crystals. | | Uses | Lead arsenate [Pb3(AsO4)4] is a toxic commercial insecticide and herbicide. | | Uses | Insecticide; veterinarian treatment as a teniacide and insecticide. | | Uses | As constituent of various insecticides for larvae of gypsy moth, boll weevil, etc. | | Definition | ChEBI: Lead arsenate is an inorganic lead salt composed from lead(2+) and arsenate dianion. It was widely used in the United States in the 1950's as an insecticide to control pests in fruit orchards, specifically apples and cherries. It has a role as an insecticide, a plant growth regulator and a rodenticide. It contains a lead(2+) and an arsenate(2-). | | Production Methods | Lead arsenate is produced mainly from lead acetate, lead nitrate, and lead oxide and disodium arsenate.The direct reaction of arsenic acid with litharge in the presence of nitric acid gives a dilead arsenate. Com mercial lead arsenates contain mostly PbHAsO4 along with varying amounts of Pb3(AsO4)2. Accordingly, their lead content is higher and their As2O3 content lower than the levels calculated for PbHAsO4. | | Health Hazard | Exposures to lead arsenate occur in work areas and it is absorbed into the body by inhalation
of its dust and by ingestion. It is irritating to the eyes, the skin, and the respiratory
tract, and causes adverse effects on the gastrointestinal tract, nervous system, kidneys,
liver, and blood. Accidental ingestion of lead arsenate in the workplace causes cough,
sore throat, abdominal pain, diarrhea, drowsiness, headache, nausea, vomiting, muscular
cramp, constipation, excitation, and disorientation in the worker. | | Potential Exposure | Used as an insecticide, herbicide, and
in manufacture of drugs; veterinary tapeworm medicine.
Incompatibilities: Violent reactions occur from contact
with oxidizers, chemically active metals; strong acids.
Acids and acid mists cause the release of arsine, a deadly
gas. Decomposes above 270�C forming toxic fumes including arsenic and lead compounds | | Shipping | UN1617 Lead arsenates, Hazard Class: 6.1;
Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials | | Incompatibilities | Used as an insecticide, herbicide, and
in manufacture of drugs; veterinary tapeworm medicine.
Incompatibilities: Violent reactions occur from contact
with oxidizers, chemically active metals; strong acids.
Acids and acid mists cause the release of arsine, a deadly
gas. Decomposes above 270�C forming toxic fumes including arsenic and lead compounds | | Waste Disposal | Long- term storage in large,
weatherproof, and sift-proof storage bins or silos; may be
disposed of by conversion to soluble salt, such as chloride,
precipitation as sulfide and return to supplier |
| | LEAD ARSENATE Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|