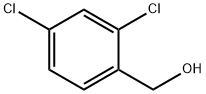
2,4-Dichlorobenzyl alcohol: pharmacological action and applications
May 20,2025
Introduction
2,4-Dichlorobenzyl alcohol (Figure 1) is a mild antiseptic with a broad spectrum for bacterial and virus associated with mouth and throat infections. 2,4-Dichlorobenzyl alcohol is considered as an active ingredient found in several marketed OTC products by Health Canada which has categorized this agent as an anatomical therapeutic chemical. On the other hand, 2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol is categorized by the FDA in the inactive ingredient for approved drug products.[1]

Pharmacodynamics
In vitro studies with the combination of 2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol and amylmetacresol have shown a virucidal against a number of viruses associated with the common cold which is observed by a reduction in the viral load.[2] In clinical trials, administration of 2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol lozenges has been shown to generate a reduced throat soreness and to provide pain relief and relief from difficulty in swallowing 5 minutes after administration. This effect can last for even 2 hours. The relief effect was shown to reach a steady-state after 45 minutes.
Mechanism of action
The use of 2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol has been related to its antibacterial, antiviral and local anesthetic properties. The local anesthetic action of 2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol is thought to be due to a reduced sodium channel blockade.[2] The antiseptic mechanism of action of 2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol is not fully understood but it is thought to be related to a denaturation of external proteins and rearrangement of the tertiary structure proteins.[3]
Prenatal developmental toxicity study of 2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol in rats
2,4-Dichlorobenzyl alcohol is a mild antiseptic with a wide range of effects on bacterial and viral oral and throat infections, and sore throat lozenges, containing 2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol, are marketed as OTC drugs in many countries. Thus, human beings, including pregnant women, can be easily exposed to it via the oral route.Therefore, in this study, we evaluated its potential effects on pregnant rats and embryo-fetal development. Different doses of 2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol (0, 25, 100, 400, and 800 mg/kg/day) were administered to SD rats daily using an oral gavage from GD 6 to 19. Thereafter, all the live dams were sacrificed on gestation day (GD) 20, and caesarean sections were conducted. Live fetuses and their placenta were weighed and then examined for external, visceral, and skeletal malformations and variations. The effects of 2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol on clinical signs, body weight, food consumption, clinical pathology, macroscopically visible characteristics, organ weights, histopathology, cesarean section, and fetal morphology were investigated during pregnancy. Based on the results obtained, dams at 800 mg/kg/day showed systemic toxicities, including a decrease in body weight and food consumption, and liver changes. Additionally, this treatment induced decreases in fetal and placental weights, as well as the increased incidence of retarded ossifications and full supernumery rib, and the decreased number of ossification centers. Therefore,based on these findings, the no-observed-adverse-effect level of 2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol was determined to be 400 mg/kg/day for dams and prenatal development.[4]
Basis and Application research
Spectrum of bactericidal action of amylmetacresol/2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol[5]
Pharyngitis is commonly caused by a self-limiting upper respiratory tract infection(URTI) and symptoms typically include sore throat. Antibiotics are often inappropriately used for the treatment of pharyngitis, which can contribute to antimicrobial resistance, therefore nonantibiotic treatments which have broad antiseptic effects may be more appropriate. Amylmetacresol (AMC) and 2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol (DCBA) are present in some antiseptic lozenges and have established benefits in providing symptomatic relief and some in vitro antiviral action.Methods: Seven bacterial species associated with pharyngitis, namely Streptococcus pyogenes,Fusobacterium necrophorum, Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis, Moraxella catarrhalis, Haemophilus influenza, Arcanobacterium haemolyticum and Staphylococcus aureus,were exposed to an AMC/DCBA lozenge dissolved in artificial saliva. In vitro bactericidal activity was measured as a log reduction in colony-forming units (CFUs).Results: Bactericidal activity was recorded against all organisms after 1 minute. Greater than 3 log10 reductions in CFUs were observed at 1 minute for S. pyogenes (log10 reduction CFU/mL±SD, 5.7±0.1), H. influenza (6.1±0.1), A. haemolyticum (6.5±0.0) and F. necrophorum (6.5±0.0),at 5 minutes for S. dysgalactiae (6.3±0.0) and M. catarrhalis (5.0±0.9) and at 10 minutes for S. aureus (3.5±0.1). Conclusion: An AMC/2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol lozenge demonstrated a greater than 99.9% reduction in CFUs against all tested species within 10 minutes, which is consistent with the time a lozenge remains in the mouth. Patients with uncomplicated bacterial pharyngitis may benefit from the antibacterial action of antiseptic AMC/2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol lozenges. Furthermore, AMC/DCBA lozenges may be more relevant and appropriate than antibiotics for pharyngitis associated with a self-limiting viral URTI.
Effectiveness of amylmetacresol and 2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol[6]
All AMC/DCBA throat lozenges containing the two core active ingredients: amylmetacresol (AMC;0.6 mg) and 2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol (DCBA;1.2 mg); both possess antibacterial, antiviral and local anesthetic properties. Amylmetacresol and 2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol throat lozenges have been marketed in many countries worldwide for pain relief in acute sore throat. Amylmetacresol and 2,4- dichlorobenzyl alcohol throat lozenges have been shown to be safe and efficient in relieving of acute sore throat symptoms, and it produces an immediate symptomatic relief. Local symptomatic pain relief plays an important role in managing acute sore throat. In-vitro evidence has demonstrated the virucidal effect of AMC and DCBA on a number of viruses associated with the common cold; a reduction in viral load is believed to have benefits in reducing the symptoms. The local anesthetic action of AMC/DCBA throat lozenges, a combination of the potent channel blocker-AMC and the reduced potency for sodium channel blockade 2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol-attenuate the effects of AMC, possibly as a result of competitive binding, which acts on a sodium channel blocker, and may be effective in relieving symptoms due to inflammation. Therefore, AMC/DCBA throat lozenge is thought to represent a useful option to meet patients’ needs and avoid unnecessary prescription of antibiotics.
Lozenges containing AMC/2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol have been reported in several clinical trials in adults and have demonstrated significant greater improvement for symptomatic and pain relief, such as difficulty swallowing and throat numbness, and a reduction in the severity of throat soreness in patients with upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs), thus allowing patients to resume their daily activities.Nowadays, more emphasis is being given on the quality of a patient’s sore throat functional daily activities,which has increased the incidence of antibiotics resistance in the community.
References
[1]Oxford JS, Lambkin R, Gibb I, Balasingam S, Chan C, Catchpole A: A throat lozenge containing amyl meta cresol and dichlorobenzyl alcohol has a direct virucidal effect on respiratory syncytial virus, influenza A and SARS-CoV. Antivir Chem Chemother. 2005;16(2):129-34. doi: 10.1177/095632020501600205. (PubMed ID 15889535)
[2]Tan TW, Chen BC, Tan HL, Chang CM: Effectiveness of amylmetacresol and 2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol throat lozenges in patients with acute sore throat due to upper respiratory tract infection: a systematic review protocol. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2017 Apr;15(4):862-872. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-003034.
[3]https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB13269
[4]Moon KN, Baek SK, Kim W, et al. Prenatal developmental toxicity study of 2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol in rats. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2022;132:105168. doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2022.105168
[5]Matthews D, Atkinson R, Shephard A. Spectrum of bactericidal action of amylmetacresol/2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol lozenges against oropharyngeal organisms implicated in pharyngitis. Int J Gen Med. 2018;11:451-456. Published 2018 Nov 28. doi:10.2147/IJGM.S184406
[6]Tan TW, Chen BC, Tan HL, Chang CM. Effectiveness of amylmetacresol and 2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol throat lozenges in patients with acute sore throat due to upper respiratory tract infection: a systematic review protocol. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2017;15(4):862-872. doi:10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-003034
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
Supplementation with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate monohydrate can synthesize neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, maintaining a healthy nervous system.....
Nov 4,2025Biochemical EngineeringPiperonylic acid is a natural molecule bearing a methylenedioxy function that closely mimics the structure of transcinnamic acid. Here is biological activity.....
May 20,2025Chemical Materials2,4-Dichlorobenzyl alcohol
1777-82-8You may like
- Application research of 4-Methylpyridin-2-amine
Nov 13, 2025
- 3-Chloropropiophenone: synthesis and application
Nov 11, 2025
- Report on 2-bromonaphthalene
Nov 4, 2025
2,4-Dichlorobenzyl alcohol manufacturers
- 2,4-Dichlorobenzyl alcohol
-
- 2025-11-27
- CAS:1777-82-8
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 0.99
- Supply Ability:
- 2,4-Dichlorobenzyl alcohol
-

- $0.00 / 25KG
- 2025-11-27
- CAS:1777-82-8
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 10 mt
- 2,4-Dichlorobenzyl alcohol
-

- $5.00 / 1KG
- 2025-09-25
- CAS:1777-82-8
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: g-kg-tons, free sample is available