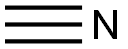시안화수소
|
|
시안화수소 속성
- 녹는점
- -13.4°
- 끓는 점
- bp 25.6°
- 밀도
- d(gas) 0.941 (air = 1); d(liq) 0.687
- 증기압
- 750 mmHg at 25 °C
- 굴절률
- 1.2594
- 용해도
- very soluble in H2O, ethanol; soluble in ethyl ether
- 물리적 상태
- 무색의 액체
- 산도 계수 (pKa)
- 9.2(at 25℃)
- 색상
- colorless liquid or gas
- 냄새
- Bitter almond odor detectable at 1 to 5 ppm; however, 20 to 60% of the population are reported to be unable to detect the odor of HCN
- 수용성
- H2O, 알코올과 혼화성; 난용성 에테르 [MER06]
- 노출 한도
- Ceiling 11 mg/m3 (10 ppm) (ACGIH), 5 mg CN/m3/10 min (NIOSH); TWA air 11 mg/m3 (10 ppm) skin (OSHA); IDLH 50 ppm.
- Dielectric constant
- 158.0(0℃)
- LogP
- -0.250
안전
- 위험 및 안전 성명
- 위험 및 사전주의 사항 (GHS)
| 위험품 표기 | F+,T+,N | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 위험 카페고리 넘버 | 12-26-50/53-26/27/28 | ||
| 안전지침서 | 7/9-16-36/37-38-45-60-61 | ||
| 유엔번호(UN No.) | 1051 | ||
| 자연 발화 온도 | 538 °C | ||
| 위험 등급 | 6.1(a) | ||
| 포장분류 | I | ||
| 유해 물질 데이터 | 74-90-8(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| 독성 | LC50 in rats, mice, dogs: 544 ppm (5 min), 169 ppm (30 min), 300 ppm (3 min) by inhalation, K. C. Back et al., Reclassification of Materials Listed as Transportation Health Hazards (TSA-20-72-3; PB214-270, 1972) | ||
| IDLA | 50 ppm | ||
| 기존화학 물질 | KE-20190 | ||
| 유해화학물질 필터링 | 97-1-90 | ||
| 사고대비 물질 필터링 | 8 | ||
| 함량 및 규제정보 | 물질구분: 사고대비물질; 혼합물(제품)함량정보: 시안화 수소 및 이를 1% 이상 함유한 혼합물 |
시안화수소 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
개요
Hydrocyanic acid, HCN, is corrosive in addition to toxic. It is also a dangerous fire and explosion risk. It has a wide flammable range of 6%–41% in air. The boiling point is 79°F (26°C), the flash point is 0°F, and the ignition temperature is 1004°F (540°C). It is toxic by inhalation and ingestion and through skin absorption. The TLV of hydrocyanic acid is 10 ppm in air. It is used in the manufacture of acrylonitrile, acrylates, cyanide salts, dyes, rodenticides, and other pesticides.화학적 성질
Water-white liquid at temperatures below 26.5C; faint odor of bitter almonds. Usual commercial material is 96–99% pure.Soluble in water. The solution is weakly acidic, sensitive to light. When not absolutely pure or stabilized, hydrogen cyanide polymerize물리적 성질
Colorless liquid or gas; odor of bitter almond; burns in air with a blue flame;refractive index 1.2675; autoignition temperature 538°C; vapor density at31°C 0.947 (air=1); liquid density 0.715 g/mL at 0°C and 0.688 g/mL at 20°C;boils at 25.7°C; melts at 13.24°C; vapor pressure 264 torr at 0°C; critical tem-perature 183.5°C; critical pressure 53.20 atm; critical volume 139 cm3/moldielectric constant 158.1 at 0°C and 114.9 at 20°C; conductivity 3.3 mhos/cmat 25°C; viscosity 0.201 centipoise at 20°C; surface tension 19.68 dyn/cm;readily mixes with water and alcohols; density of a 10% aqueous solution0.984 g/mL at 20°C; pKaat 25°C 9.21.출처
Peaches, apricots, bitter almonds, cherries, and plums contain some HCN derivatives in their kernels, frequently in combination with glucose and benzaldehyde as a glucoside (amygdalin). The bitter almond fragrance of HCN and its derivatives sometimes can be detected in such kernels.역사
Hydrogen cyanide in pure form was prepared first in 1815 by Gay-Lussac.Earlier, in 1782, Scheel prepared this compound in dilute solution. The mostimportant application of hydrogen cyanide is to produce methyl methacrylatefor methacrylate resins and plastics. Other products made from hydrogencyanide include potassium cyanide, sodium cyanide, adiponitrile, methionine,cyanuric chloride, cyanogen, nitrilotriacetic acid, and several triazine pesti-cides. The compound also is used in small amounts for extermination ofrodents.용도
HCN was first isolated from a blue dye, Prussian blue, in 1704. HCN is obtainable from fruits that have a pit, such as cherries, apricots, and bitter almonds, from which almond oil and flavouring are made. HCN is used in fumigating, electroplating, mining, and producing synthetic fibres, plastics, dyes, and pesticides. It also is used as an intermediate in chemical syntheses.Besides, hydrogen cyanide is used in manufacturing cyanide salts, aerylonitrile,and dyes.It is also used as a horticultural fumigant.
제조 방법
Hydrogen cyanide is generally produced in industrial quantities by hightemperature catalytic reaction between ammonia, methane, and air (theAndrussow process). The stoichiometry of the process is:2CH4 + 2NH3 + 3O2 → HCN + 3H2O ΔHrxn = 230.4 kcal
The above reaction is endothermic requiring a temperature of 1,100°C and acatalyst such as platinum or rhodium. Other hydrocarbons may be usedinstead of methane.
The compound may be made by several other methods, which include:1. Heating methanol and ammonia in the absence of air at elevated temperatures (600 to 950°C) using a catalyst:
CH3OH + NH3 → HCN + H2O + H2
2. Thermal decomposition of formamide at elevated temperatures and reduced pressure:
HCONH2 → HCN + H2O
3. Heating acetonitrile and ammonia at 1,100 to 1,300°C:
CH3CN + NH3 → 2HCN +2H2
4. Reaction of sodium cyanide or potassium cyanide or potassium ferrocyanide with a mineral acid:
NaCN + HCl → HCN + NaCl
K4Fe(CN)6 + 6HCl → 6HCN + 4KCl + FeCl2
정의
ChEBI: A one-carbon compound consisting of a methine group triple bonded to a nitrogen atom. Also known as formonitrile, hydrogencyanide and prussic acid,HCN is a highly toxic liquid that has the odor of bitter almonds and boils at 25.6 °C.also known as hydrocyanic acid, prussic acid, and fonnonitrile, is a very poisonous colorless gas with a characteristic fragrance of bitter almonds. Small amounts of hydrogen cyanide derivatives in combination with glucose and benzaldehyde are found in nature in apricot,peach,cherry, and plum pits.It liquifies at 26°C (79 OF) and is soluble in water,alcohol,and ether. Hydrogen cyanide is usually sold commercially as an aqueous solution containing 2 to 10% hydrogen cyanide. HCN reacts with amines, oxidisers, acids, sodium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide, sodium carbonate, caustic substances, and ammonia. The aqueous solutions of hydrogen cyani dedecompose slowly to form anunonium formate. In some uses, it is preferable to generate hydrogen cyanide as needed, thus eliminating handling and storage problems.
생산 방법
Hydrogen cyanide has been manufactured from sodium cyanide and mineral acid and from formamide by catalytic dehydration. Two synthesis processes account for most of the hydrogen cyanide produced. The dominant commercial process for direct production of hydrogen cyanide is based on classic technology involving the reaction of ammonia, methane (natural gas), and air over a platinum catalyst; it is called the Andrussow process. The second process, which involves the reaction of ammonia and methane, is called the Blaus€aure–Methan–Ammoniak (BMA) process; it was developed by Degussa in Germany. Hydrogen cyanide is also obtained as a by-product in the manufacture of acrylonitrile by the ammoxidation of propylene (Sohio process).화학 반응
Hydrogen cyanide reacts with hydrogen at 140 °C in the presence of a catalyst, e.g., platinum black, to form methyl amine CH3NH2. When burned in air, it produces a pale violet flame; when heated with dilute sulfuric acid, it forms formamide HCONH2 and ammonium formate HCOONH4; when exposed to sunlight with chlorine it forms cyanogen chloride CNCl, plus hydrogen chloride. An important reaction of hydrogen cyanide is that with aldehydes or ketones, whereby cyanhydrins are formed, e.g., acetaldehyde cyanhydrin CH3CHOH·CH, and the resulting cyanhydrins are readily converted into alpha-hydroxy acids, e.g., alphahydroxypropionic acid CH3·CHOH·COOH.일반 설명
Hydrocyanic acid solution is water containing up to 5% dissolved hydrocyanic acid with the faint odor of almonds. HYDROGEN CYANIDE is toxic by inhalation and skin absorption. Prolonged exposure to low concentrations or short term exposure to high concentrations may result in adverse health effects. Its vapors are just barely lighter than air.반응 프로필
This particular record contains hydrogen cyanide dissolved in water. Hydrogen cyanide is a very volatile liquid or colorless gas smelling of bitter almonds, b.p. 26° C. A deadly human poison by all routes. The gas (hydrogen cyanide) forms explosive mixtures with air, HYDROGEN CYANIDE reacts violently with acetaldehyde. HYDROGEN CYANIDE is a severe explosion hazard when heated or exposed to oxidizers. HYDROGEN CYANIDE may polymerize explosively at elevated temperature (50-60° C) or in the presence of traces of alkali [Wohler, L. et al., Chem. Ztg., 1926, 50, p. 761, 781]. In the absence of a stabilizer (e.g., phosphoric acid) HYDROGEN CYANIDE may undergo explosively rapid spontaneous (autocatalytic) polymerization leading to a fire. The reaction is autocatalytic because of ammonia formation. The anhydrous acid should be stabilized by the addition of acid. [Bond, J., Loss Prev. Bull., 1991, 101, p.3]. During the preparation of imidoester hydrochlorides, hydrogen chloride was rapidly passed over alcoholic hydrogen cyanide. An explosion ensued, even with cooling of the process, [J. Org. Chem., 1955, 20, 1573].위험도
Flammable, dangerous fire risk, explosive limits in air 6–41%. Toxic by ingestion, inhalation, and skin absorption. TLV: ceiling 4.7 ppm.건강위험
Exposures to hydrogen cyanide cause adverse health effects to animals and humans. Hydrogen cyanide is readily absorbed from the lungs and the symptoms of poisoning begin within seconds to minutes. The symptoms of toxicity and poisoning include, but are not restricted to, asphyxia, lassitude or weakness, exhaustion, headache, confusion, nausea, vomiting, increased rate and depth of respiration, or respiration slow and gasp- ing, thyroid and blood changes. Inhalation of hydrogen cyanide causes headache, dizzi- ness, confusion, nausea, shortness of breath, convulsions, vomiting, weakness, anxiety, irregular heart beat, tightness in the chest, and unconsciousness, and these effects may be delayed. The target organs of induced toxicity and poisoning include the CNS, cardiovas- cular system, thyroid, and blood.화재위험
Hydrogen cyanide is a highly flammable liquid. Liquid HCN contains a stabilizer (usually phosphoric acid), and old samples may explode if the acid stabilizer is not maintained at a sufficient concentration.인화성 및 폭발성
Hydrogen cyanide is a highly flammable liquid. Liquid HCN contains a stabilizer (usually phosphoric acid), and old samples may explode if the acid stabilizer is not maintained at a sufficient concentration.저장
Hydrogen cyanide should be stored in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area in tightly sealed containers and with the correct label. Containers of hydrogen cyanide should be protected from physical damage and should be stored separately from amines and oxidizers, such as perchlorates, peroxides, permanganates, chlorates, and nitrates. It should be kept sepa- rated from strong acids, such as hydrochloric, sulfuric, and nitric acids, away from sodium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide, sodium carbonate, water, ammonia, acetaldehyde, and caustics.Purification Methods
HCN is prepared from NaCN and H2SO4, and dried by passage through H2SO4 and over CaCl2, then distilled in a vacuum system and degassed at 77oK before use [Arnold & Smith J Chem Soc, Faraday Trans 2 77 861 1981]. Cylinder HCN may contain stabilisers against explosive polymerisation, together with small amounts of H3PO4, H2SO4, SO2, and water. It can be purified by distillaton over P2O5, then frozen in Pyrex bottles at Dry-ice temperature for storage. [Zeigler Org Synth Coll Vol I 314 1941, Glemser in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry (Ed. Brauer) Academic Press Vol I pp 658-660 1963.] Liquid HCN, like liquid ammonia, evaporates very slowly since the latent heat of evaporation is high and keeps it in the liquid state because the temperature of the liquid is lowered to below its boiling point. EXTREMELY POISONOUS; all due precautions should be taken.비 호환성
HCN can polymerize explosively if heated above 50 °C or in the presence of trace amounts of alkali.폐기물 처리
In the event of a spill, remove all ignition sources. Cleanup should be conducted wearing appropriate chemical-resistant clothing and respiratory protection Disposal Excess hydrogen cyanide and waste material containing this substance should be placed in an appropriate container, clearly labeled, and handled according to your institution's waste disposal guidelines. For more information on disposal procedures, see Chapter 7 of this volume.주의 사항
Occupational workers should be very careful in the management of HCN since the gas in air is explosive at concentrations over 5.6%, equivalent to 56,000 ppm and it does not provide adequate warning of hazardous concentrations. HCN at a concentration of 300 mg/m3 in air becomes fatal within about 10 min and HCN at a concentration of 3500 ppm (about 3200 mg/m3 ) kills a human in about 1 min.시안화수소 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
준비 용품
시안화수소 관련 검색:
2,3-디클로로-5,6-디시아노-1,4-벤조퀴논 시클로프로필시아니드 수소 디아미노말레오니트릴 사이아나이드 이온 사이안화 나트륨 사이안화 칼륨
TERT-BUTYL ISOCYANIDE
9-Anthrracenecarbonitrile
1,1,3,3-TETRAMETHYLBUTYL ISOCYANIDE
METHYL ISOCYANOACETATE
1-CYCLOPENTENYLACETONITRILE
1-Phenyl-1-cyclopentanecarbonitrile
Benzyl isocyanide
Ethyl isocyanoacetate
9-CYANOPHENANTHRENE
9-DICYANOMETHYLENE-2,4,7-TRINITROFLUORENE
1-Benzocyclobutenecarbonitrile