- glucosylglycerol
-

- $0.00 / 1kg
-
2026-02-13
- CAS:22160-26-5
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 1000kg
- glucosylglycerol
-

- $0.10 / 1KG
-
2025-12-24
- CAS:22160-26-5
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99.0%
- Supply Ability: 1000 tons
|
| Product Name: | glucosylglycerol | | Synonyms: | glucosylglycerol;2-O-α-D-Glucosylglycerol;Extremys GG;GLYCERYL GLUCOSIDE;Glycoin;GG;2-O-α-D-Glucosylglycerol:Glucosylglycerol:Extremys GG:Glycoin:GLYCERYL GLUCOSIDE;Skycore AGG | | CAS: | 22160-26-5 | | MF: | C9H18O8 | | MW: | 254.23 | | EINECS: | 824-773-6 | | Product Categories: | 22160-26-5 | | Mol File: | 22160-26-5.mol | 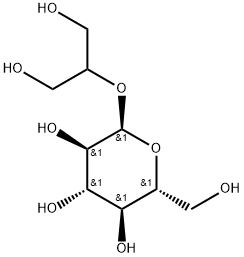 |
| | glucosylglycerol Chemical Properties |
| Melting point | 121 °C | | Boiling point | 606.1±55.0 °C(Predicted) | | density | 1.58±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) | | vapor pressure | 0.022Pa | | storage temp. | Hygroscopic, Refrigerator, under inert atmosphere | | solubility | Methanol (Slightly), Water (Slightly, Sonicated) | | form | Solid | | pka | 12.85±0.70(Predicted) | | color | White to Off-White | | Stability: | Very Hygroscopic | | Cosmetics Ingredients Functions | HUMECTANT
SKIN CONDITIONING | | InChI | InChI=1/C9H18O8/c10-1-4(2-11)16-9-8(15)7(14)6(13)5(3-12)17-9/h4-15H,1-3H2/t5-,6-,7+,8-,9+/s3 | | InChIKey | AQTKXCPRNZDOJU-QHXZDXPMNA-N | | SMILES | O([C@@H]1[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1)O)C(CO)CO |&1:1,2,3,5,7,r| | | LogP | -3.46 |
| | glucosylglycerol Usage And Synthesis |
| Structure | According to the stereo conformation of glycosidic linkages, naturally occurring Glucosylglycerols (GGs) are generally divided into α-GGs and β-GGs. Whereas α-GGs are mainly identified in microorganisms during their responses to environmental stresses, to date, β-GGs are found exclusively in higher plants. | | Description |
Glucosylglycerols (GGs) are a group of small heterosides comprising one molecule of glucose and one molecule of glycerol via glycosidic bonds. In nature, glycosidic linkages within GGs are established between the C1-hydroxyl group of glucose and one of the three hydroxyl groups of sn-glycerol. They are mainly produced by many moderately salt-tolerant cyanobacteria as compatible solutes in a salt-dependent manner and synthesized in a few higher plants and fermentation processes. Because of their many interesting physicochemical properties and biological activities, such as low sweetness, low hygroscopicity, high water-holding capacity, excellent biocompatibility, favourable performance in protecting macromolecules, and antitumor activity, GGs exhibit large application potential in the fields of cosmetics, health care, food service, enzyme production, and pharmaceuticals[1].
| | Uses | 2-O-α-D-Glucosylglycerol is used to prepare glycoglycerolipid analogs active as antitumor-promoters the influence of the anomeric configuration. | | Definition | ChEBI: 2-O-(alpha-D-glucopyranosyl)glycerol is a glucosylglycerol consisting of an alpha-D-glucosyl residue attached at position 2 of glycerol via a glycosidic bond. It has a role as an osmolyte and a bacterial metabolite. It is a glucosylglycerol and an alpha-D-glucoside. | | Synthesis | Glucosylglycerol is extracted and purified from microalgae culture. Steps include: 1) Harvesting and washing of microalgal cells. 2) Homogenization and primary dehydration of cells. 3) Three-stage counter-current extraction to obtain an extract containing GG. 4) Filtration of the extract to remove impurities. 5) Two-stage pigment removal (membrane separation and adsorption resin). 6) Membrane concentration and desalination. 7) Dehydration to obtain high-purity GG product. | | References | [1] Quan Luo, Xuefeng Lu, Yangkai Duan . “Biological sources, metabolism, and production of glucosylglycerols, a group of natural glucosides of biotechnological interest.” Biotechnology advances 59 (2022): Article 107964. |
| | glucosylglycerol Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|