Lamivudine Impurities 173829-09-9
Product Number: L013019
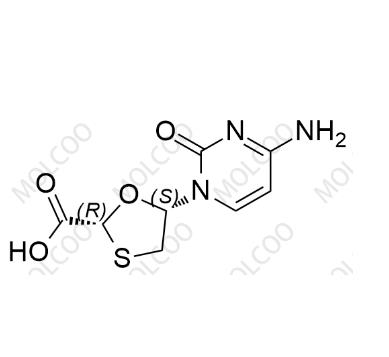
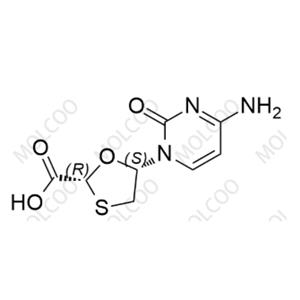
English Name: Lamivudine Impurities 19
English Alias: (2R,5S)-5-(4-amino-2-oxopyrimidin-1(2H)-yl)-1,3-oxathiolane-2-carboxylic acid
CAS Number: 173829-09-9
Molecular Formula: C₈H₉N₃O₄S
Molecular Weight: 243.24
Product Advantages:
High-purity standard:HPLC purity ≥99.0%, with structure confirmed by multiple methods including 1H NMR, 13C NMR, ESI-MS, and elemental analysis, meeting the technical requirements of pharmacopoeias such as USP and EP for impurity reference standards.
Excellent stability:Stable for 24 months when stored at 2-8°C in the dark, with a degradation rate <1% after 7 days at room temperature in solution (e.g., methanol-water mixture), suitable for long-term quality control and complex analytical scenarios.
Precise chiral configuration:With a defined (2R,5S) configuration, it accurately matches the detection needs of chiral impurities in lamivudine APIs, avoiding quantitative deviations caused by racemic interference.
Applications:
Pharmaceutical impurity detection:Used for HPLC or LC-MS detection of Impurities 19 in lamivudine APIs and formulations, controlling its content ≤0.1% in accordance with ICH Q3A standards to ensure compliance with international quality specifications.
Synthesis process optimization:In the chiral cyclization reaction of lamivudine, monitoring impurity content (e.g., reducing impurity from 0.9% to 0.1% when chiral catalyst dosage increases from 0.8mol% to 1.2mol%) optimizes reaction conditions to inhibit by-product formation.
Analytical method development:Serves as a chiral impurity reference standard for establishing specific detection methods, such as normal-phase HPLC using a Chiralpak AD-H column to achieve effective separation and accurate quantification of enantiomers.
Toxicological research support:Provides standard samples for evaluating the potential toxicity of chiral impurities, facilitating in vitro cytotoxicity tests and in vivo pharmacokinetic studies to meet FDA, EMA, and other regulatory requirements for impurity safety assessment.
Background Description:
Lamivudine Impurities 19 are chiral impurities introduced during lamivudine (a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor) synthesis due to incomplete chiral center construction or cyclization side reactions. This impurity has a similar structure to the parent drug but different configuration, potentially affecting the drug's antiviral activity and safety. According to the ICH Q6A guideline, chiral drugs require strict control of enantiomeric impurities, making precise detection and limit control of this impurity a core aspect of lamivudine quality research. Current pharmacopoeias mandate qualitative identification and quantitative analysis of such chiral impurities, typically setting individual impurity limits ≤0.1%.
Research Status:
Advances in detection technology:The mainstream method is chiral HPLC using a cellulose derivative chiral column (e.g., Chiralcel OD-H), with n-hexane-ethanol-trifluoroacetic acid (70:30:0.1, v/v) as the mobile phase, detection wavelength at 254nm, and a limit of quantitation (LOQ) of 0.02%. LC-MS/MS combined with chiral selectors can reduce the detection limit to 0.05μg/mL, suitable for trace impurity screening.
Formation mechanism research:This impurity mainly originates from insufficient chiral induction in thiazolidine cyclization reactions. Impurity formation increases significantly at reaction temperatures above 25°C or in highly polar solvents (e.g., DMSO). Using low temperature (0-5°C) and chiral ligands (e.g., diethyl tartrate) in the reaction can reduce impurity content to below 0.05%.
Safety evaluation:In vitro antiviral activity tests show that the impurity has only 5% of the HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitory activity of lamivudine, but mild liver enzyme elevation was observed in high-dose groups (100mg/kg) during a 28-day rat toxicity test, suggesting that reasonable limits (e.g., ≤0.08%) should be set based on toxicological data.












 China
China