Isovanillin: Metabolism and its Potencial anticancer activities research
Apr 30,2025
Introduction
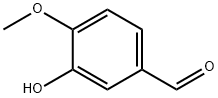
Isovanillin (3-Hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde; Figure 1) is a natural product found in many plant species like Plucheasagittalis, Pycnocycla spinose, Mondia whitei, Benincasahispida, Arum Palaestinum, Thalictrum przewalskii, Valeriana officinalis var. latifolia. [1] Chemically, it is a phenolic aldehyde isomer of vanillin that possesses antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer activity. The anticancer effect of isovanillin results in part from binding the active sites of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV (CAMKIV), which regulates apoptosis, cell cycle control, and cell signaling activities through phosphorylation and dephosphorylation processes. Isovanillin is a selective inhibitor but not a substrate for the aldehyde oxidase enzyme and is metabolized into isovanillic acid byaldehyde dehydrogenase.[2]

Metabolism of isovanillin
Aromatic aldehydes are good substrates of aldehyde dehydrogenase activity but are relatively poor substrates of aldehyde oxidase and xanthine oxidase. However, the oxidation of xenobiotic-derived aromatic aldehydes by the latter enzymes has not been studied to any great extent. The present investigation compares the relative contribution of aldehyde dehydrogenase, aldehyde oxidase and xanthine oxidase activities in the oxidation of isovanillin in separate preparations and also in freshly prepared and cryopreserved liver slices. The oxidation of isovanillin was also examined in the presence of specific inhibitors of each oxidizing enzyme. Minimal transformation of isovanillin to isovanillic acid was observed in partially purified aldehyde oxidase, which is thought to be due to residual xanthine oxidase activity. Isovanillin was rapidly metabolized to isovanillic acid by high amounts of purified xanthine oxidase, but only low amounts are present in guinea pig liver fraction. Thus the contribution of xanthine oxidase to isovanillin oxidation in guinea pig is very low. In contrast, isovanillin was rapidly catalyzed to isovanillic acid by guinea pig liver aldehyde dehydrogenase activity. The inhibitor studies revealed that isovanillin was predominantly metabolized by aldehyde dehydrogenase activity. The oxidation of xenobiotic-derived aromatic aldehydes with freshly prepared or cryopreserved liver slices has not been previously reported. In freshly prepared liver slices, isovanillin was rapidly converted to isovanillic acid, whereas the conversion was very slow in cryopreserved liver slices due to low aldehyde dehydrogenase activity. The formation of isovanillic acid was not altered by allopurinol, but considerably inhibited by disulfiram. It is therefore concluded that isovanillin is predominantly metabolized by aldehyde dehydrogenase activity, with minimal contribution from either aldehyde oxidase or xanthine oxidase.[3]
Potencial anticancer activities research
1.Radioiodination, nasal nanoformulation and preliminary evaluation of isovanillin: A new potential brain cancer-targeting agent
Brain cancer is a challenging disease to treat using conventional approaches. The present investigation aimed to develop a radio pharmaceutical targeting brain cancer based on natural isovanillin. Different parameters were optimized, resulting in high radiolabeling efficiency (97.3± 1.2%) and good stability (<48 h). The tracer was formulated for intranasal delivery in a chitosan nanoparticles system with a mean particle size of 141±2 nm, a polydispersity index of 0.23± 0.02, and a zeta potential of -17.4 ± 0.3 mV to enhance nasal uptake and surmount the blood-brain barrier. The system was characterized and assessed in-vitro for suitability and specificity and evaluated in-vivo in normal and tumorized mice. The biodistribution profile in brain tumor showed 20.5±0.4% ID/g localization and cancer cell targeting within 60 min. Improvement in brain tumor uptake resulted from both the nanoformulation and nasal administration of iodoisovanillin. Overall, the reported results encourage the potential use of the nanoformulated labeled compound as an anticancer agent.[2]
2. Arum Palaestinum with isovanillin, linolenic acid and beta-sitosterol inhibits prostate cancer spheroids and reduces the growth rate of prostate tumors in mice.
Background: Arum palaestinum is a plant commonly found in the Middle East that is ingested as an herbal remedy to fight cancer. However, no studies have examined the direct effect of the plant/plant extract on tumor growth in an animal model. Verified prostate cancer cells were plated as 3D spheroids to determine the effect of extract from boiled Arum Palaestinum Boiss roots. In addition, male NU/NU mice (8 weeks old) with xenograft tumors derived from the prostate cancer cell line were treated daily with 1000 mg/kg body weight gavage of the suspension GZ17. The tumor growth was measured repeatedly with calipers and the excised tumors were weighed at the termination of the 3 week study. Control mice (10 mice in each group) received vehicle in the same manner and volume.
Results: The number of live prostate cancer cells declined in a dose/dependent manner with a 24 h exposure to the extract at doses of 0.015 to 6.25 mg/mL. A fortified version of the extract (referred to as GZ17) that contained higher levels of isovanillin, linolenic acid and β-sitosterol had a stronger effect on the cell death rate, shifting the percentage of dead cells from 30% to 55% at the highest dose while the vehicle control had no effect on cell numbers. When GZ17 was applied to non-cancer tissue, in this case, human islets, there was no cell death at doses that were toxic to treated cancer cells. Preliminary toxicity studies were conducted on rats using an up-down design, with no signs of toxic effect at the highest dose. NU/NU mice with xenograft prostate tumors treated with GZ17 had a dramatic inhibition of tumor progression, while tumors in the control group grew steadily through the 3 weeks. The rate of tumor volume increase was 73 mm(3)/day for the vehicle group and 24mm(3)/day for the GZ17 treated mice. While there was a trend towards lower excised tumor weight at study termination in the GZ17 treatment group, there was no statistical difference. Fortified Arum palaestinum Boiss caused a reduction in live cells within prostate cancer spheroids and blocked tumor growth in xenografted prostate tumors in mice without signs of toxicity.[4]
References
[1] de Carvalho AC, Girola N, de Figueiredo CR, et al. Understanding the cytotoxic effects of new isovanillin derivatives through phospholipid Langmuir monolayers. Bioorg Chem. 2019;83:205-213. doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2018.10.029
[2] El-Kawy OA, Shweeta HA, Attallah KM. Radioiodination, nasal nanoformulation and preliminary evaluation of isovanillin: A new potential brain cancer-targeting agent. Appl Radiat Isot. 2022;189:110464. doi:10.1016/j.apradiso.2022.110464
[3] Panoutsopoulos GI, Beedham C. Metabolism of isovanillin by aldehyde oxidase, xanthine oxidase, aldehyde dehydrogenase and liver slices. Pharmacology. 2005;73(4):199-208. doi:10.1159/000082860
[4] Cole C, Burgoyne T, Lee A, Stehno-Bittel L, Zaid G. Arum Palaestinum with isovanillin, linolenic acid and β-sitosterol inhibits prostate cancer spheroids and reduces the growth rate of prostate tumors in mice [published correction appears in BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015 Sep 14;15:322. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0854-6.]. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015;15:264. Published 2015 Aug 5. doi:10.1186/s12906-015-0774-5
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
4,7-Dichloroquinoline is encountered as an organic intermediate in the manufacture of chloroquine and other quinoline derivatives.....
Apr 29,2025Pharmaceutical intermediatesXanthone is a heterocyclic compound with a dibenzo-γ-pyrone framework and well-known to have "privileged structures" for anticancer activities.....
Apr 30,2025APIIsovanillin
621-59-0You may like
- Isovanillin
-

- $0.00 / 25Kg/Bag
- 2025-08-08
- CAS:621-59-0
- Min. Order: 1Kg/Bag
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 20ton
- Isovanillin
-

- $0.00 / 25kg
- 2025-07-25
- CAS:621-59-0
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 10000KGS
- Isovanillin
-

- $0.00 / 1KG
- 2025-06-27
- CAS:621-59-0
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 500000kg