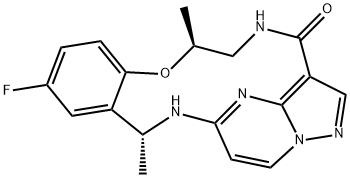
Repotrectinib: A New Anti-cancer Drug
Sep 29,2025
Over 85% of lung cancer cases are non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and ROS1 rearrangement is an actionable target alteration that occurs in 1 to 2% of patients with NSCLC. Repotrectinib is an oral inhibitor of ROS1, and it represents the first approved targeted therapy that specifically includes patients previously treated with a ROS1 TKI in FDA labeling.[1]
Mechanism of Action
Repotrectinib is an inhibitor of proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase ROS1 (ROS1) and of the tropomyosin receptor tyrosine kinases (TRKs) TRKA, TRKB, and TRKC. Fusion proteins that include ROS1 domains can drive tumorigenic potential through hyperactivation of downstream signaling pathways leading to unconstrained cell proliferation. Repotrectinib exhibited antitumor activity in cultured cells expressing ROS1 fusions and mutations including SDC4-ROS1, SDC4-ROS1G2032R, CD74-ROS1, CD74-ROS1G2032R, CD74-ROS1D2033N, and CD74-ROS1L2026M.[2]
The Efficacy of Repotrectinib
The Safety results demonstrate clinically meaningful durable antitumor activity of repotrectinib in both ROS1 TKI-naïve and ROS1 TKI-pretreated (1 prior ROS1 TKI with no chemotherapy or immunotherapy) patients with ROS1-positive NSCLC. The efficacy of repotrectinib was consistent across prespecified subgroups (in patients with CNS metastasis and resistance mutations) and supported by sustained durability of responses given an additional 6 months of follow-up, providing substantial evidence of antitumor activity over time. Efficacy was generally consistent across subgroups by age, sex, and race without meaningful differences in durable responses.
The Safety of Repotrectinib
Ocular toxicity is a known effect of drugs in this class, and there was a signal of visual adverse events in the clinical trial. Among the 351 patients treated with repotrectinib at the RP2D, vision disorders occurred in 12%, including Grade 3 to 4 in 0.3%. Most visual disorder AEs were reported as low grade. Eye and vision exams were not included in the TRIDENT-1 protocol and vision disorders were thus not adequately characterized in the safety dataset. A post-marketing requirement (PMR) was issued to conduct a prospective study to evaluate risk factors, manifestations, and outcomes associated with the potential safety signal of serious ocular toxicity with repotrectinib in patients with ROS1-positive NSCLC or other solid tumors on study.[3]
The synthetic method of Repotrectinib[4]

Fig.1. The synthetic route of Repotrectinib
Step 1. To a solution of tert-butyl (R)-(2-hydroxypropyl)carbamate (1.00 g, 5.71 mmol) and tosyl chloride (1.14 g, 6.00 mmol) in DCM (29 mL) was added triethylamine (1.44 g, 14.28 mmol) and the mixture was stirred at room temp for 48 hour. The reaction solution was concentrated under reduced pressure and the residue was purified with flash chromatography (ISCO system, silica(40g), 0-20%ethyl acetate in hexane) to provide Intermediate A (1.12 g, 3.40 mmol, 59.54% yield).
Step 2. To a solution of Starting Material (100.00 mg, 0.290 mmol) and Intermediate A (143.50 mg, 0.436 mmol) in DMF (1.45 mL) was added K2CO3 (200.7 mg, 1.45 mmol) and heated at 80 °C with stirring for 16 hour. The reaction was cooled to ambient temperature and diluted with DCM (3 mL), filtered through a syringe filter, and concentrated under reduced pressure. Flash chromatography (ISCO system, silica (12 g), 0-60% ethyl acetate in hexane) provided Intermediate B (32.90 mg, 0.0656 mmol, 22.59% yield).
Step 3. To a solution of Intermediate B (32.90 mg, 0.0656 mmol) in MeOH (3 mL) and THF (2 mL) was added LiOH aqueous solution (2M, 2 mL) at ambient temperature. The reaction solution was heated at 70 °C for 2 hours. The reaction flask was cooled to ambient temperature, diluted with water and methanol, and then quenched with HCl aqueous solution (2 M, 2 mL) to pH <5. The mixture was extracted with DCM (3x5 mL), dried with Na2SO4. Concentrated under reduced pressure and dried on high vacuum overnight. To a solution of the acid product in DCM (4 mL) was added 4 M HCl in 1,4-dioxane (2.0 mL). The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 3 hours, and then concentrated under reduced pressure and dried on high vacuum. To a solution of the de-Boc product and FDPP (27.62 mg, 0.0719 mmol) in DMF (1.6 mL) was added Hunig's base (42.23 mg, 0.327 mmol) at room temperature. The mixture was stirred for 2.5 hours, and then quenched the reaction with 2 M Na2CO3 solution (2 mL). The mixture was stirred for 15 min then extracted with DCM (4x10 mL). The combined extracts were dried with Na2SO4 and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified with flash chromatography (ISCO system, silica (12 g), 0-10% methanol in dichloromethane) to provide repotrectinib (10.1 mg, 0.0284 mmol, 43.49% yield for three steps).
References
[1]Rikova K, Global survey of phosphotyrosine signaling identifies oncogenic kinases in lung cancer. Cell. 2007;131(6):1190-203.
[2]U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Drugs@FDA [database on the internet]. Repotrectinib USPI.
[3]U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Drugs@FDA [database on the internet]. Repotrectinib Approval Letter.
[4]Cui, Jingrong Jean, Diaryl macrocycles as modulators of protein kinases and their preparation, [P] WO2015112806.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
Explores DEGDBE's solvent properties, polyurethane applications, density data, and related toxicity concerns in industrial use.....
Sep 29,2025Organic ChemistryDodecylpyridinium chloride are used in a wide variety of applications,of which application research examples are reported here.....
Sep 29,2025Chemical MaterialsRepotrectinib
1802220-02-5You may like
- Repotrectinib/TPX-0005
-

- $2.00 / 1kg
- 2025-09-30
- CAS:1802220-02-5
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 50KG/M
- Repotrectinib
-

- $45.00 / 1mg
- 2025-09-29
- CAS:1802220-02-5
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 99.92%
- Supply Ability: 10g
- Repotrectinib
-

- $0.00 / 25kg
- 2025-09-29
- CAS:1802220-02-5
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 98%
- Supply Ability: 1000kg