
Ergosterol synthesis
- Product Name:Ergosterol
- CAS Number:57-87-4
- Molecular formula:C28H44O
- Molecular Weight:396.65
![4a,13b-Etheno-1H,9H-benzo[c]cyclopenta[h][1,2,4]triazolo[1,2-a]cinnoline-1,3(2H)-dione, 6,8-bis(acetyloxy)-5,6,7,8,8a,8b,10,10a,11,12,13,13a-dodecahydro-11-(2-hydroxy-1-methylethyl)-8a,10a-dimethyl-2-phenyl-, [4aS-[4aα,6α,8β,8aα,8bβ,10aα,11α(R*),13aβ,13bα]]- (9CI)](/CAS/20211123/GIF/125315-55-1.gif)
125315-55-1
0 suppliers
inquiry

57-87-4
477 suppliers
$30.00/1g
Yield:-
Steps:
Multi-step reaction with 9 steps
1: pyridine / 4 h / Ambient temperature
2: 1) NaI / 1) DMF, 30 min, 80 deg C, 2) 30 min, 80 deg C
3: 79 percent / KOH / methanol / 0.5 h / Heating
4: 90 percent / PPTS / CH2Cl2 / 24 h / Ambient temperature
5: 1) BuLi, HMPA / 1) THF, -78 deg C to -20 deg C, 20 min, 2) THF, -20 deg C, 1.5h
6: 53 percent / sodium amalgam (5percent), Na2HPO4 / methanol / 16 h / Ambient temperature
7: 83 percent / p-TsOH*H2O, 95percent EtOH / 4 h / 80 °C
8: 86 percent / LiAlH4 / tetrahydrofuran / Heating
9: 25 percent / diethyl ether; tetrahydrofuran / 0.05 h / Irradiation
References:
Tsuji;Yokoyama;Tachibana;Ikekawa [Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan,1990,vol. 63,# 8,p. 2233 - 2238]
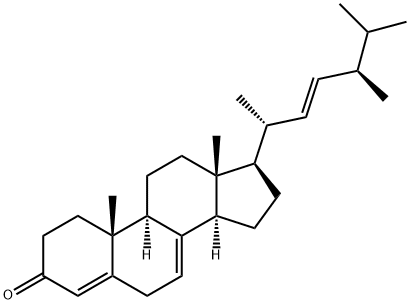
17398-57-1
3 suppliers
inquiry

57-87-4
477 suppliers
$30.00/1g
![4a,13b-Etheno-1H,9H-benzo[c]cyclopenta[h][1,2,4]triazolo[1,2-a]cinnoline-1,3(2H)-dione, 6-(benzoyloxy)-5,6,7,8,8a,8b,10,10a,11,12,13,13a-dodecahydro-8a,10a-dimethyl-11-(1,4,5-trimethyl-2-hexenyl)-, [4aS-[4aα,6α,8aα,8bβ,10aα,11α(1S*,2E,4S*),13aβ,13bα]]- (9CI)](/CAS/20240320/GIF/87530-75-4.gif)
87530-75-4
0 suppliers
inquiry

57-87-4
477 suppliers
$30.00/1g
![4a,13b-Etheno-1H,9H-benzo[c]cyclopenta[h][1,2,4]triazolo[1,2-a]cinnoline-11-acetaldehyde, 6,8-bis(acetyloxy)-2,3,5,6,7,8,8a,8b,10,10a,11,12,13,13a-tetradecahydro-α,8a,10a-trimethyl-1,3-dioxo-2-phenyl-, [4aS-[4aα,6α,8β,8aα,8bβ,10aα,11α(R*),13aβ,13bα]]- (9CI)](/CAS/20211123/GIF/125315-53-9.gif)
125315-53-9
0 suppliers
inquiry

57-87-4
477 suppliers
$30.00/1g