Bempedoic Acid Impurity
WhatsAPP: +86 17320513646
E-mail: anna@molcoo.com
Product Information:
Product Number: B079022
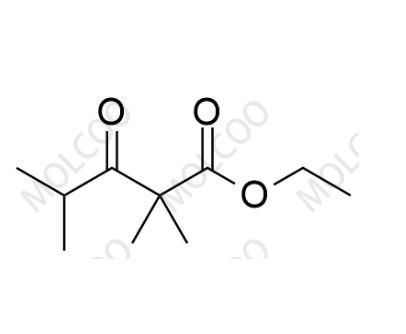
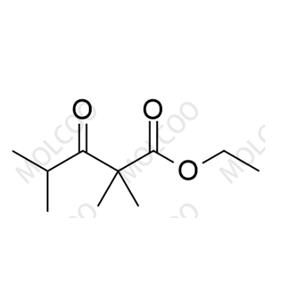
English Name: Bempedoic Acid Impurity 22
English Alias: ethyl 2,2,4-trimethyl-3-oxopentanoate
CAS Number: 4447-64-7
Molecular Formula: C₁₀H₁₈O₃
Molecular Weight: 186.25
Advantages:
High purity and structural confirmation:HPLC purity ≥99.0%, with structure verified by 1H NMR, 13C NMR, and HRMS, complying with ICH Q2(R1) standards, suitable as an official reference standard for qualitative and quantitative impurity analysis.
Outstanding stability:Stable for 36 months when stored at -20°C in the dark, with a degradation rate <1% after heating at 60°C for 72 hours in solution (e.g., acetonitrile-water system), suitable for high-temperature accelerated testing and long-term quality control.
Process-specific impurity:As a characteristic impurity from condensation reactions or decarboxylation side reactions in bempedoic acid synthesis, it accurately tracks process risks of insufficient alkylation reagent selectivity during keto-ester condensation.
Applications:
Pharmaceutical impurity detection:Used for LC-MS/MS detection of Impurity 22 in bempedoic acid APIs and formulations, controlling its content ≤0.1% in accordance with ICH Q3A standards to ensure compliance with international regulatory limits for process impurities.
Synthesis process optimization:In condensation reactions, monitoring impurity content (e.g., changing the catalyst to boron trifluoride diethyl ether to reduce impurity from 1.1% to 0.1%) optimizes reaction conditions to minimize alkylation by-product formation.
Analytical method development:Serves as a keto-ester impurity reference standard for establishing specific detection methods, such as ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS), achieving accurate quantification using characteristic fragment ions (m/z 155.1→113.0) (detection limit LOD=0.005ppm).
Toxicological research support:Provides samples for evaluating the potential toxicity of keto-ester impurities, facilitating in vitro liver microsome metabolism assays and in vivo pharmacokinetic studies to clarify their impact on drug metabolic pathways.
Background Description:
During bempedoic acid synthesis, ethyl 2,2,4-trimethyl-3-oxopentanoate (Impurity 22) may be introduced due to insufficient regioselectivity in keto-ester condensation reactions or decarboxylation. The impurity’s α-ketoester group may affect drug metabolic stability and increase potential hepatotoxicity risks. According to the ICH M7 (R1) guideline, impurities with electrophilic groups require strict genotoxicity assessment. Current industry standards set the individual impurity limit at ≤0.1%.
Research Status:
Advances in detection technology:UPLC-MS/MS is employed using a C18 ultra-hydrophobic column (1.7μm, 2.1×100mm) with 0.1% formic acid aqueous solution-acetonitrile (gradient elution) as the mobile phase, combined with multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode, achieving a limit of quantitation (LOQ) as low as 0.01μg/mL for precise trace impurity detection.
Formation mechanism analysis:This impurity mainly originates from excessive alkylation reagent (e.g., methyl iodide) addition during condensation reactions or decarboxylation under acidic conditions. Reacting under low-temperature (-10°C) and weak base (e.g., potassium carbonate) conditions can reduce impurity formation by over 90%.
Safety evaluation:In vitro Ames tests showed no mutagenicity at concentrations ≤200μg/dish, but serum ALT elevation was observed in high-dose groups (150mg/kg) during canine repeated dosing tests, suggesting that reasonable limits (e.g., ≤0.06%) should be set based on toxicological data to ensure drug safety.
WhatsAPP: +86 17320513646
E-mail: anna@molcoo.com
NEW IN STOCK!
The Molcoo Laboratory added drug impurity reference standards, including Baricitinib, Piperazine, Benzylpenicillin, Tranilast and multiple N-Nitroso drug impurities! Now available for immediate delivery!










 China
China