|
|
| | LDN-57444 Basic information |
| Product Name: | LDN-57444 | | Synonyms: | LDN-57444;5-Chloro-1-[(2,5-dichlorophenyl)methyl]-1H-indole-2,3-dione3-(O-acetyloxime);LDN-57444/LDN57444;1H-Indole-2,3-dione, 5-chloro-1-[(2,5-dichlorophenyl)methyl]-, 3-(O-acetyloxime);5-Chloro-1-[(2,5-dichlorophenyl)methyl]-1H-indole-2,3-dione 3-(O-acetyloxime) LDN 57444;3-(O-acetyloxime), 5-chloro-1-[(2,5-dichlorophenyl)methyl]-1H-Indole-2,3-dione;UCH-L1 Inhibitor;(Z)-3-(Acetoxyimino)-5-chloro-1-(2,5-dichlorobenzyl)indolin-2-one | | CAS: | 668467-91-2 | | MF: | C17H11Cl3N2O3 | | MW: | 397.64 | | EINECS: | | | Product Categories: | Inhibitors | | Mol File: | 668467-91-2.mol | 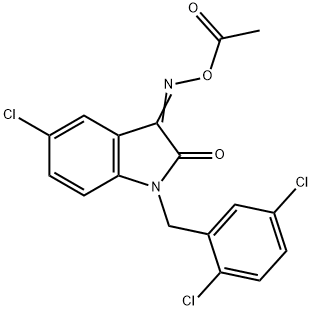 |
| | LDN-57444 Chemical Properties |
| Boiling point | 534.4±60.0 °C(Predicted) | | density | 1.50±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) | | storage temp. | 2-8°C | | solubility | DMSO: soluble16mg/mL | | form | solid | | pka | -2.57±0.20(Predicted) | | color | Yellow | | Stability: | Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20° for up to 1 week. | | InChI | 1S/C17H11Cl3N2O3/c1-9(23)25-21-16-13-7-12(19)3-5-15(13)22(17(16)24)8-10-6-11(18)2-4-14(10)20/h2-7H,8H2,1H3/b21-16- | | InChIKey | OPQRFPHLZZPCCH-PGMHBOJBSA-N | | SMILES | CC(=O)O\N=C1/C(=O)N(Cc2cc(Cl)ccc2Cl)c3ccc(Cl)cc13 |
| Hazard Codes | N | | Risk Statements | 50/53 | | Safety Statements | 60-61 | | RIDADR | UN 3077 9 / PGIII | | WGK Germany | 3 | | Storage Class | 11 - Combustible Solids |
| | LDN-57444 Usage And Synthesis |
| Description | The ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCH-L1) is a member of a family of de-ubiquitinating enzymes that can generate free ubiquitin from ubiquitin precursors via its ubiquitin ligase activity. By associating with free ubiquitin, it also prevents its degradation. Neuronal UCH-L1 has been linked to Parkinson’s disease, the development of tumors, and neuropathic pain. LDN-57444 is an inhibitor of UCH-L1 activity (IC50 = 0.88, Ki = 0.4 μM) that demonstrates selectivity for UCH-L1 compared to UCH-L3 (IC50 = 25 μM). Loss of UCH-L1 activity causes cell death through the apoptosis pathway due to an impaired ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. LDN-57444-induced reduction of free ubiquitin has been shown to create dramatic alterations in synaptic structure and function, increasing spine size while decreasing spine density in hippocampal neurons. | | Uses | LDN 57444 is an inhibitor of UCH-L1, an enzyme expressed by certain lung tumor-derived cell lines, suggesting that this enzyme plays a role in tumor progression. | | Biochem/physiol Actions | LDN-57444 is a potent, reversible, competitive and active site-directed inhibitor of UCHL1 | | in vivo | LDN-57444 (0.4 mg/kg, i.p.) blocks the beneficial effect of V-Uch-L1, and worsens contextual conditioning performance as the mice are exposed to the context at 1, 7, 14, and 21 days after training[2]. | | References | [1] YICHIN LIU. Discovery of inhibitors that elucidate the role of UCH-L1 activity in the H1299 lung cancer cell line.[J]. Chemistry & biology, 2003, 10 9: 837-846. DOI:10.1016/j.chembiol.2003.08.010
[2] YU-YAN TAN. Endoplasmic reticulum stress contributes to the cell death induced by UCH-L1 inhibitor.[J]. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 2008, 318 1-2: 109-115. DOI:10.1007/s11010-008-9862-x
[3] ANNA E CARTIER. Regulation of synaptic structure by ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1.[J]. Journal of Neuroscience, 2009, 29 24: 7857-7868. DOI:10.1523/jneurosci.1817-09.2009 |
| | LDN-57444 Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|